






















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
important notes of Digital electronics
Typology: Study notes
1 / 29

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!






















A memory is just like a human brain. It is used to store data and instruction. Computer memory is the storage space in computer where data is to be processed and instructions required for processing are stored. The memory is divided into large number of small parts. Each part is called a cell. Each location or cell has a unique address which varies from zero to memory size minus one. For example if computer has 64k words, then this memory unit has 64 * 1024 = 65536 memory location. The address of these locations varies from 0 to 65535. ❖ Classification of Memories Memory is the most essential element of a computing system because without it computer can’t perform simple tasks. Computer memory is of two basic type –
It can be reprogrammed. The EPROM can be erased by exposing it to ultra- violet light for a duration of upto 40 minutes. To reprogram it, erase all the previous data. Usually, an EPROM eraser achieves this function. During programming an electrical charge is trapped in an insulated gate region. The charge is retained for more than ten years because the charge has no leakage path. For erasing this charge, ultra-violet light is passed through a quartz crystal window (lid). This exposure to ultra-violet light dissipates the charge. During normal use the quartz lid is sealed with a sticker.
logical memory from physical memory. This separation allows an extremely large virtual memory to be provided for programmers when only a smaller physical memory is available.
7. Auxiliary Memory Auxiliary memory is much larger in size than main memory but is slower. It normally stores system programs, instruction and data files. It is also known as secondary memory. It can also be used as an overflow/virtual memory in case the main memory capacity has been exceeded. Secondary memories cannot be accessed directly by a processor. First the data/information of auxiliary memory is transferred to the main memory and then that information can be accessed by the CPU. Characteristics of Auxiliary Memory are following − - Non-volatile memory − Data is not lost when power is cut off. - Reusable − The data stays in the secondary storage on permanent basis until it is not overwritten or deleted by the user. - Reliable − Data in secondary storage is safe because of high physical stability of secondary storage device. - Convenience − With the help of a computer software, authorised people can locate and access the data quickly. - Capacity − Secondary storage can store large volumes of data in sets of multiple disks. - Cost − It is much lesser expensive to store data on a tape or disk than primary memory.
Difference between Primary Memory and Secondary Memory: BASIS FOR COMPARISON
Basic Primary memory is directly accessible by Processor/CPU. Secondary memory is not directly accessible by CPU. Altered Name Main memory. Auxiliary memory. Data Instructions or data to be currently executed are copied to main memory. Data to be permanently stored is kept in secondary memory. Volatility Primary memory is usually volatile. Secondary memory is non- volatile. Formation Primary memories are made of semiconductors. Secondary memories are made of magnetic and optical material. Access Speed Accessing data from primary memory is faster. Accessing data from secondary memory is slower. Access Primary memory is accessed by the data bus. Secondary memory is accessed by input-output channels. Size The computer has a small primary memory. The computer has a larger secondary memory. Expense Primary memory is costlier than secondary memory. Secondary memory is cheaper than primary memory Memory Primary memory is an internal memory. Secondary memory is an external memory.
Difference between Volatile Memory and Non-Volatile Memory: S.NO VOLATILE MEMORY NON-VOLATILE MEMORY
Difference between RAM and ROM: BASIS FOR COMPARISON
Basic It is a read-write memory. It is read only memory. Use Used to store the data that has to be currently processed by CPU temporarily. It stores the instructions required during bootstrap of the computer. Volatility It is a volatile memory. It is a nonvolatile memory. Stands for Random Access Memory. Read Only Memory. Modification Data in RAM can be modified. Data in ROM can not be modified. Capacity RAM sizes from 64 MB to 4GB. ROM is comparatively smaller than RAM. Cost RAM is a costlier memory. ROM is comparatively cheaper than RAM. Type Types of RAM are static RAM and dynamic RAM. Types of ROM are PROM, EPROM, EEPROM. Difference between SRAM and DRAM: BASIS FOR COMPARISON
Speed Faster Slower Size Small Large Cost Expensive Cheap Used in Cache memory Main memory Density Less dense Highly dense Construction Complex and uses transistors and latches. Simple and uses capacitors and very few transistors. Single block of memory requires 6 transistors Only one transistor. Charge leakage property Not present Present hence require power refresh circuitry Power consumption Low High
Difference between EPROM and EEPROM: BASIS FOR COMPARISON
Basic Ultraviolet Light is used to erase the content of EPROM. EEPROM contents are erased using electronic signal. Appearance EPROM has a transparent quartz crystal window at the top. EEPROM are totally encased in an opaque plastic case. Erased and Reprogrammed EPROM chip has to be removed from the computer circuit to erase and reprogram the computer BIOS. EEPROM chip can be erased and reprogrammed in the computer circuit to erase and reprogram the content of computer BIOS. Technology EPROM is an older technology. EEPROM is a modern version over EPROM.
Programmable Logic Devices (PLDs) are the integrated circuits. They contain an array of AND gates & another array of OR gates. There are three kinds of PLDs based on the type of array(s), which has programmable feature.
Here, 3 to 8 decoder generates eight min terms. The two programmable OR gates have the access of all these min terms. But, only the required min terms are programmed in order to produce the respective Boolean functions by each OR gate. The symbol ‘X’ is used for programmable connections.
PAL is a programmable logic device that has Programmable AND array & fixed OR array. The advantage of PAL is that we can generate only the required product terms of Boolean function instead of generating all the min terms by using programmable AND gates. The block diagram of PAL is shown in the following figure.
Here, the inputs of AND gates are programmable. That means each AND gate has both normal and complemented inputs of variables. So, based on the requirement, we can program any of those inputs. So, we can generate only the required product terms by using these AND gates. Here, the inputs of OR gates are not of programmable type. So, the number of inputs to each OR gate will be of fixed type. Hence, apply those required product terms to each OR gate as inputs. Therefore, the outputs of PAL will be in the form of sum of products form. Example Let us implement the following Boolean functions using PAL. A=XY+XZ' A=XY'+YZ' The given two functions are in sum of products form. There are two product terms present in each Boolean function. So, we require four programmable AND gates & two fixed OR gates for producing those two functions. The corresponding PAL is shown in the following figure.
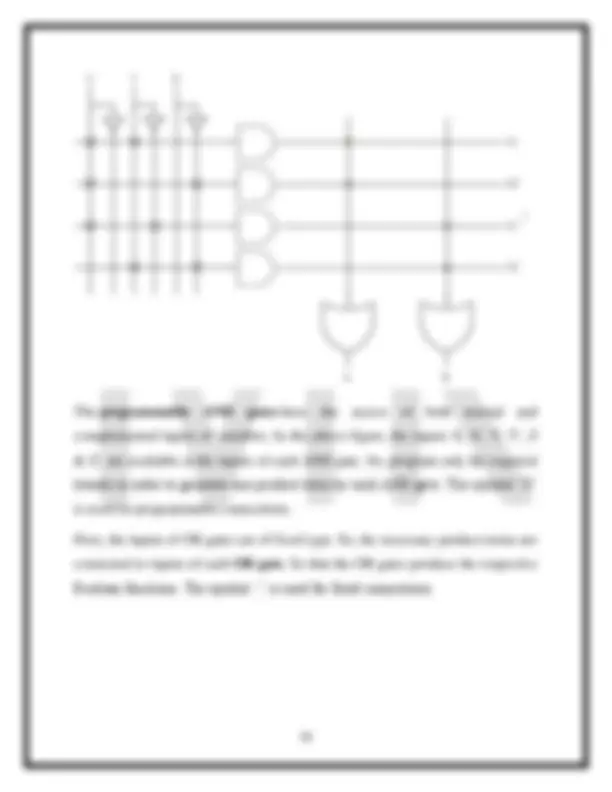
PLA is a programmable logic device that has both Programmable AND array & Programmable OR array. Hence, it is the most flexible PLD. The block diagram of PLA is shown in the following figure. Here, the inputs of AND gates are programmable. That means each AND gate has both normal and complemented inputs of variables. So, based on the requirement, we can program any of those inputs. So, we can generate only the required product terms by using these AND gates. Here, the inputs of OR gates are also programmable. So, we can program any number of required product terms, since all the outputs of AND gates are applied as inputs to each OR gate. Therefore, the outputs of PAL will be in the form of sum of products form. Example Let us implement the following Boolean functions using PLA. A=XY+XZ' B=XY'+YZ+XZ'
The given two functions are in sum of products form. The number of product terms present in the given Boolean functions A & B are two and three respectively. One product term, Z'X is common in each function. So, we require four programmable AND gates & two programmable OR gates for producing those two functions. The corresponding PLA is shown in the following figure. The programmable AND gates have the access of both normal and complemented inputs of variables. In the above figure, the inputs X, X', Y, Y', Z & Z', are available at the inputs of each AND gate. So, program only the required literals in order to generate one product term by each AND gate. All these product terms are available at the inputs of each programmable OR gate. But, only program the required product terms in order to produce the respective Boolean functions by each OR gate. The symbol ‘X’ is used for programmable connections.