Download 9/11's Political Impact: Al Gore's Presidency & Bin Laden's Motives and more Slides History in PDF only on Docsity!
Lecture 21:
Impacts on the
Middle East (II)
The American
War in Iraq!
Rationales of the
Mid-term Examination
- Grade to be Posted Before Next Wednesday (Hopefully)
- Question Analysis Next Wednesday (Hopefully)
- Roles of Examinations
- Future-oriented: Grade [3-4-3]
- Enrichment-oriented: Performance [?-?-?]
- Newspaper Reader or Newspaper Commentator?
- Political Science in the Perceptive Spectrum
Political Science
(Logic, Methodology, Induction, Deduction)
History Water-blowing
(Memorization) (Subjective Bluffing)
Question 14: Which of the following countries CAN be
attacked by the United States AFTER the introduction of the
revised Bush Doctrine?
- Afghanistan.
- Iraq.
- China.
- Britain.
- All of the above.
Bush Doctrine I:
- To the USA: Passive (wait for the decision of others)
- To other Countries: Active (can decide to take side) Bush Doctrine II:
- To the USA: Active (can define the terrorist threat)
- To other Countries: Passive (cannot even take side)
Which of the following countries CAN be attacked by the United States AFTER the introduction of the original Bush Doctrine?
- None of the above. Docsity.com
Question 13: If Al Gore was elected as the American
president in 2000, which of the followings is still MOST
likely to happen after 911?
- NOT Imaginary
- The Hidden Questions:
- What is the main difference between the foreign policy of the Democratic Party (Clinton-Gore) and the Republic Party (Reagan-Bush Sr.-Bush Jr.)?
- How are the choices categorized?
- The American War against Afghanistan. [Multilateralism]
- The American War against Iraq. [Unilateralism]
- The declination of Russian membership in NATO. [Unilateralism]
- The formation of the Axis of Evil. [Unilateralism]
- All of the above are likely to happen after 911 even with Al Gore as the president.
- None of the above. a debatable option
The Methodological Training
• To differentiate the very similar facts in the newspapers,
which represent very different hidden agendas
- Bypass, cross, occupy, overcome, tackle…
• To trace the MAIN origin of different facts
contemporarily by the DEDUCTION logic
• To predict the MAIN focus of different facts
contemporarily by the INDUCTION logic
• Inter-transferability in Real Life
Announcements on Guest Speakers
- Israel Consul General Eli Avidar
- The Israeli-Palestinian Issue
- Lecture 19: 19 th^ March 2003 (Wednesday)
- http://hongkong.mfa.gov.il
- Indian Political Consul Anurag Goel
- Indian Response to 911 and the Regional Order
- Lecture 25: 31 st^ March 2003 (Monday)
- Please Sign Up for Lunch Afterwards
- Advice on Presentation of T1, 2B, 3B:
http://pshweb01.881903.com/main/event/hot/
hot20030314cr2bd.asx
PART I
The First Gulf War
(1990-1991)
Early History of Iraq
- The Glorious and “Warlike”
History of the Iraqis:
- The Babylonian Empire
- Saddam’s Idol: King Nebuchadnezzar
- The Islamic Empire and the Arabian Nights
- Iraqis under Ottoman Rule
- Message from the “Restoration”
of Babylonian Heritage by
Saddam Hussein
The Independent Iraq
• 1932: Independence of
Iraq
- King Faisal I
- Concept of “Economic
Imperialism” and “Semi-
colony”
• 1958: Military Coup
against King Faisal II
• 1961: First Modern Claim
of Kuwait by General
Qasim Docsity.com
Saddam Hussein and
the “Least Islamist Islamic Country”
- 1968: Arab Socialist Baath
(Resurrection) Party
- Purge of Islamic Fundamentalism!
- 1979: Saddam Hussein and the
Revolutionary Command
Committee (RCC)
- 1980-1988: Iran-Iraq War
- Ayatollah Khomeni and the Islamic Revolution in Iran
- Saddam Hussein as the Great Secular Leader
- CIA Support towards Iraq
International Response
• United Nations Sanction and
Condemnation
• Coalition Army of 34 Countries
- USA, Britain, NATO
- Gulf Cooperative Committee, Egypt,
Syria
• Desert Storm (Jan – April 1991)
PART II
Results of the
First Gulf War
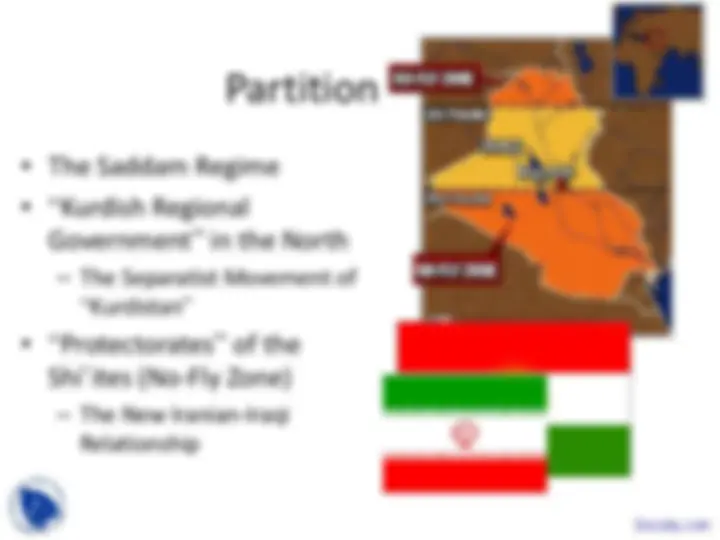
Partition of Iraq
• The Saddam Regime
• “Kurdish Regional
Government” in the North
- The Separatist Movement of
“Kurdistan”
• “Protectorates” of the
Shi’ites (No-Fly Zone)
Relationship
United Nations Sanctions
• 1990: Economic Sanctions
• 1991: End of Iraq’s Mass Destruction Weapons
• 1995: “Oil for Food” Program
• 1998: “Operation Desert Fox”
• Saddam: 1.7million deaths 1991-
• Resignation of United Nations Inspectors in Protest