









Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
User interface design and interaction
Typology: Assignments
Uploaded on 03/22/2022
5
(3)2 documents
1 / 17

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










Prototype link
1.Specify User Needs 4.Usability Testing 2.Gather Requirements 5.Implementation 3.Design Solution 6.Deployment
There following are Main Dimensions for Interaction Design.
navigation system prototype to ensure that users should easily interact with the system since words and icons responds to just a slight touch from the fingertip. (Blazquez Cano et al. , 2017) 4 D Time – The length the user takes while interacting with the 3Dimensions for the first time. This includes how users can measure progress sound and animation. In the design incorporated the 4th^ dimension through making sure that processes don’t take long to avoid long user journeys which might lead to a user not being satisfied with the system since processes take too long. 5 D Behavior - When engaging with the system, how does the user respond and feel? fifth dimension has been incorporated in the new system prototype by using simple and learnable actions such as swiping up and down to scroll tapping icons to open folder and other common gestures which are popular.
The demonstration of a vehicle entertainment and navigation system will be based on a prototype. A prototype is the initial creation of a product that demonstrates the basics of how it will look, function, and work.(Lauff, Kotys-Schwartz and Rentschler, 2018) Interaction design and cognitive psychology theories will be used with a variety of literary backgrounds to develop requirements for proposing the best prototypes to achieve the project's goals. "Interaction design theory focuses on designing meaningful ways for people to engage with things and systems, and the product of interaction is nearly completely determined by the quality of the user experience," according to the definition.(Coiera, 2003) and Cognitive psychology is defined as the branch of psychology dedicated to the study of mental processes. However, it can be difficult to understand how many different types of mental processes exist and how people use them in their own way to draw conclusions and make decisions.
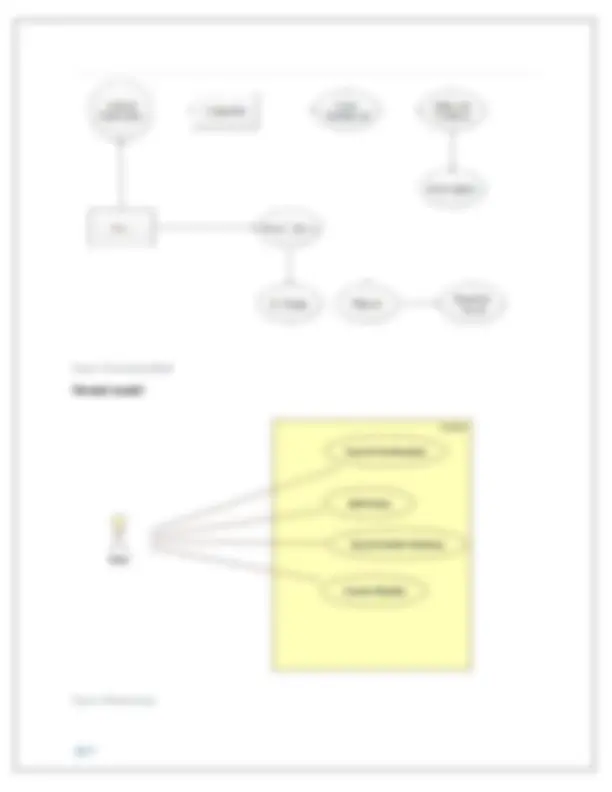
Core cognitive processes such as attention, recognition and memory have been used to come up with the recommended requirements for the new car entertainment and navigation system prototype. On features like the Music Library using an icon that is more familiar with users. The concept of attention is used to create an interface that attracts the user's attention and allows the user to understand their limits. Therefore, I decided to use GPS (Global Positioning System) for navigation. To assist have a clear idea of what kind of interface, behavior, and features to give, design theory was utilized to come up with a conceptual model and mental model for the prototype. According to (Henderson, 2002) define Conceptual model as "a high-level explanation of how a system is organized and operated". With that in mind, it's an idea that outlines what people can do with a product and what concepts they need to understand how to interact with it. The main advantage of conceptualizing a design at this level is that "designers can organize their thoughts before they start creating widgets." Below are diagrams showing the conceptual and mental model for the new Car entertainment and navigation system.
Figure 1 :Conceptual Model Mental model Figure 2 Mental image
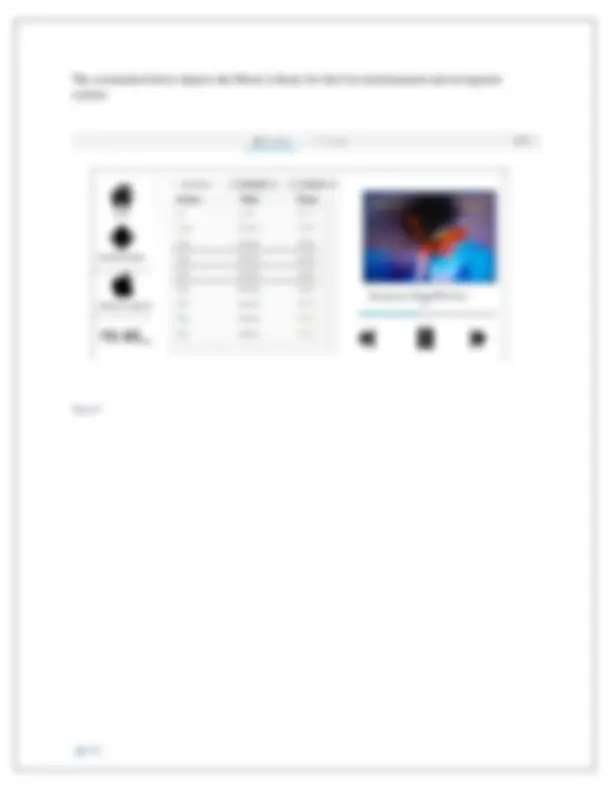
The screenshots below illustrate a low-fidelity prototype of the proposed system. Starting with the automobile entertainment and navigation system's main page. Figure 3
The screenshot below shows what occurs when you click on the Music Icon, which takes you to an interface that displays the music collection. Figure 4 The screenshot below is showing what happens after you click the Navigation Icon, it brings you to an interface which will show you navigation homepage where you can view the map. Figure 5
Different frameworks for interaction design, as well as the five dimensions of interaction design, were considered in this research. The framework implemented for the creation of the mid-fidelity prototype was user-centered design, as the coursework mandated that we primarily focus on navigation and entertainment. Research activities were carried out to develop requirements for the design, in order to produce a meaningful experience, a discussion on design principles and cognitive psychology was held, and the complete prototype was developed based on the features acquired. The limitation of the prototype is that it is only focusing on the two main areas Navigation and entertainment other functionalities are not included for example the phone and Bluetooth functions. Given the product's constraints, the following are the future developments that must be taken into account the prototype should be improved in order to build a fully functional automobile entertainment and navigation system.
Axure RP10 was used to create the prototype of the car entertainment and navigation system. Because an automobile is necessary to access the system, the car and the system will function in tandem. The following are screenshots of the Mid Fidelity Prototype: Car Entertainment and Navigation System The screenshot below depicts the user interface (UI) for the Car Entertainment and Navigation system, which showcases all icons and functions on the Homepage. Figure 6 :home page for the system
The screenshot below depicts the Navigation Panel for the Car entertainment and navigation system included a button for easy navigation to minimize user journeys. Figure 8
Beyer, H. & Holtzblatt, K., 1998. CONTEXTUAL DESIGN: Defining Customer-Centered Sysstems. s.l.:Academic Press. Goodwin, K., 2009. DESIGNING FOR THE DIGITAL AGE : HOW TO CREATE HUMAN-CENTERED PRODUCTS. s.l.:Wiley Publishing Inc. Henderson, J. J. a. A., 2002. Conceptual models: begin by designing what to design. Volume 1, pp. 25-32. Jennifer Preece, Y. R. H. S., 2002. interaction design : beyond human- computer interaction. 1st ed. s.l.:Wiley and Sons. kolko, j., 2011. Thoughts on Interaction Design. 2nd ed. s.l.:s.n. T.winograd, 1997. Challenges for human-centered Design. s.l.:s.n. Vischer, J., 2008. Towards a user-centred theory of built environment. s.l.:s.n. Blazquez Cano, M. et al. (2017) “The influence of image interactivity upon user engagement when using mobile touch screens,” Computers in Human Behavior , 77. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2017.03.042. Coiera, E. (2003) “Interaction design theory,” in International Journal of Medical Informatics. doi:10.1016/S1386-5056(02)00106-5. Lauff, C.A., Kotys-Schwartz, D. and Rentschler, M.E. (2018) “What is a prototype? what are the roles of prototypes in companies?,” Journal of Mechanical Design, Transactions of the ASME , 140(6). doi:10.1115/1.4039340. Mackenzie, I.S. (2017) “Fitts’ Law,” in The Wiley Handbook of Human Computer Interaction Set. doi:10.1002/9781118976005.ch17. Weiss, N. et al. (2020) “From Product to Platform: How can BMW compete with Platform Giants?,” Journal of Information Technology Teaching Cases , 11(2). doi:10.1177/2043886920944185.