



Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
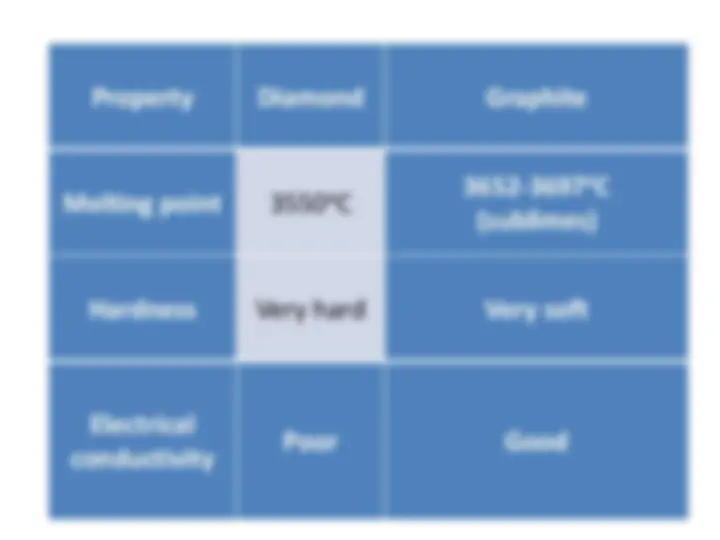
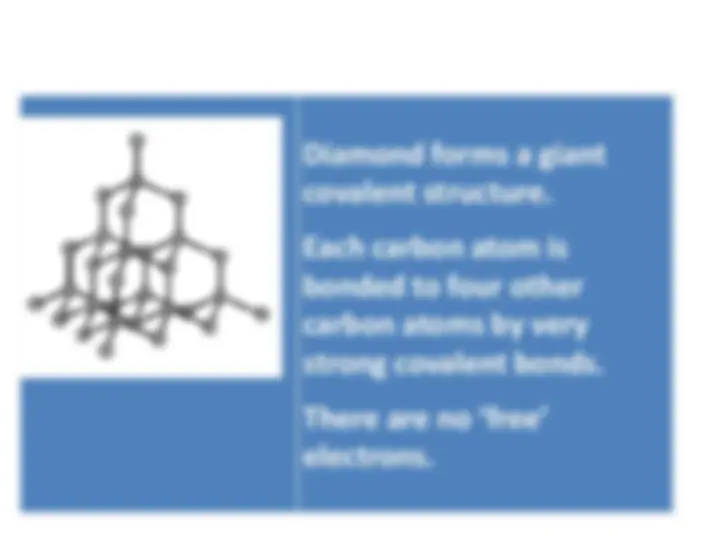
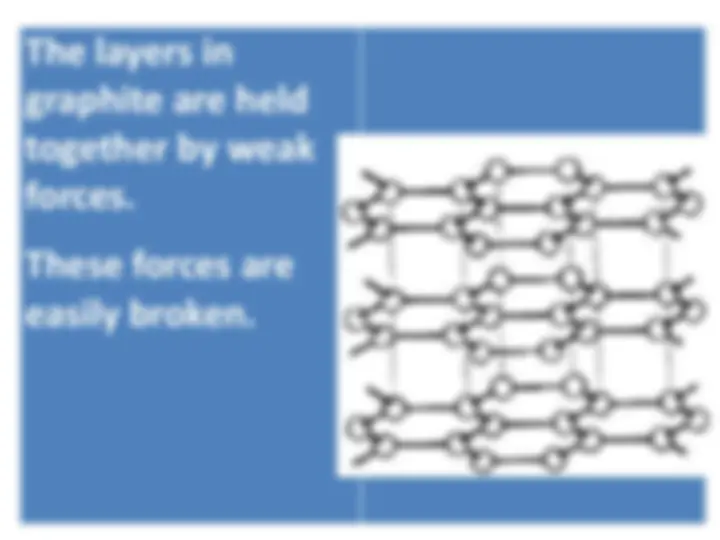
Information about the structures, properties, and uses of diamond and graphite, two forms of carbon. Diamond is known for its hardness and poor electrical conductivity, while graphite is soft, slippery, and has good electrical conductivity. Both have unique properties that make them valuable in various industries.
What you will learn
Typology: Summaries
1 / 8

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





Substance Description Picture
Diamond
A hard, clear non-metal
Graphite
A soft, slippery, grey, solid non- metal
Graphite is used for pencils and as a lubricant to reduce friction on moving surfaces.
Diamonds are used for
jewellery and in drills for
cutting through rock.