














Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This lecture is part of lecture series on subject of Project Management at Tezpur University Gate. Instructor name is Rajkumari Vishaka. It includes: Generation, Screening, Project, Ideas, Environment, Corporate, Appraisal, Preliminary, Sources, Entrepreneur
Typology: Slides
1 / 23

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
















1
2
Stimulating the flow of ideas SWOT analysis Clear articulation of objectives Cost reduction Productivity improvement Increase in capacity utilization Improve in contribution margin Expansion into promising fields Fostering a conducive work environment
4
5
7
8
10
Marketing and distribution Production and Operations Research and development Corporate resources and personnel Financing and accounting
11
Five basic competitive forces Threat of new entrants Rivalry among existing firms Pressure from substitute products Bargaining power of buyers Bargaining power of sellers
13
Analyze the performance of existing industries Examine the inputs and outputs of various industries Review imports and exports Study plan outlays and government guidelines Look at suggestions of financial institutions and development agencies Investigate local materials and resources Analyze economic and social trends
14
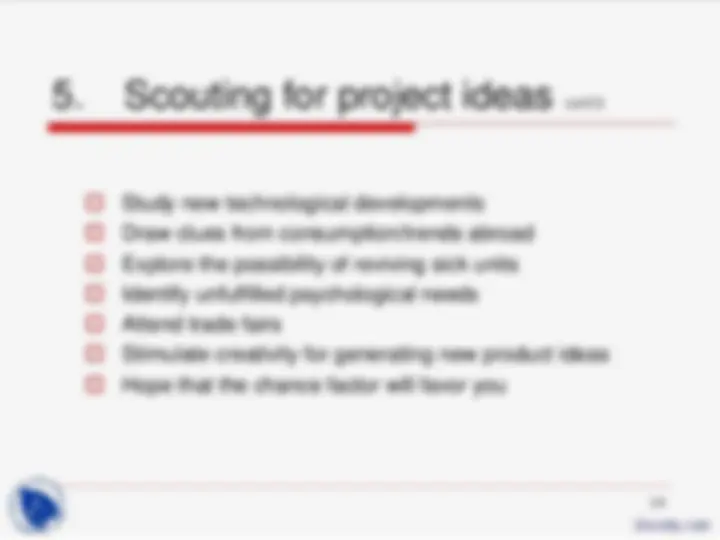
Study new technological developments Draw clues from consumption/trends abroad Explore the possibility of reviving sick units Identify unfulfilled psychological needs Attend trade fairs Stimulate creativity for generating new product ideas Hope that the chance factor will favor you
16
Construction of a Rating Index Identify factors relevant for project rating Assign weights to these factors Rate the project proposal on various factors (using a 5 or 7- point scale) For each factor, multiply the factor rating with the factor weight to get the factor score Add all the factor scores to get the overall project rating index
17
Economies of scale Product differentiation Cost advantage Marketing reach Technological edge Government policy
19
Willingness to make sacrifices Leadership Decisiveness Confidence in the project Marketing orientation Strong ego
20