




















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
In the rural development we study the following concept:Eu Rural Development, New Council Regulation, Rural Development, Commission Implementing, Rules, Preparation, Delivery Structures, Programming and Reporting, Strategic Approach, Simplification
Typology: Slides
1 / 32

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

























*Data as of 2004. World Bank estimates, using the ENIGH 2002.
Spacial Dispersion Covariance Risk
Ethnicity Issues Seasonality
No Integrated Prod. Chains
No Access to Financial Svcs.
Poverty
Migration
GOVT. BUDGET CONSTRAINTS
PRESENCE OF SUSTAINABLE FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
MARKET DEVELOPMENT
POLITICAL CONTEXT
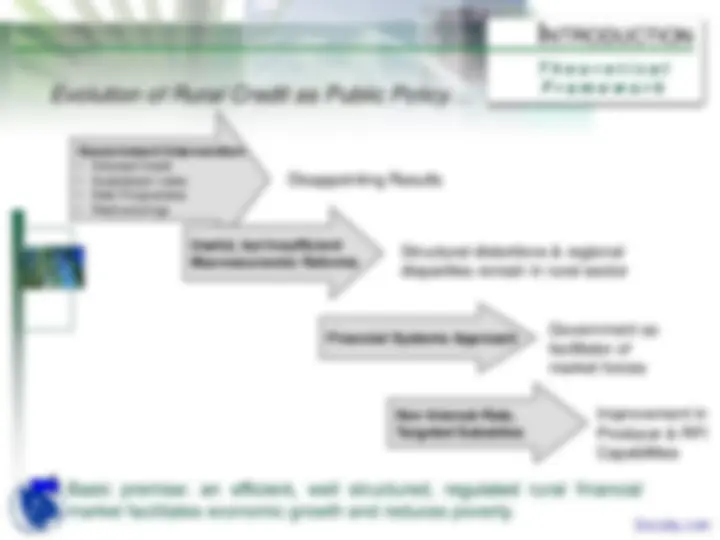
MARKET FORCES ALONE WERE NOT ENOUGH TO ACHIEVE THE PUBLIC POLICY OBJECTIVE OF RURAL DEVELOPMENT
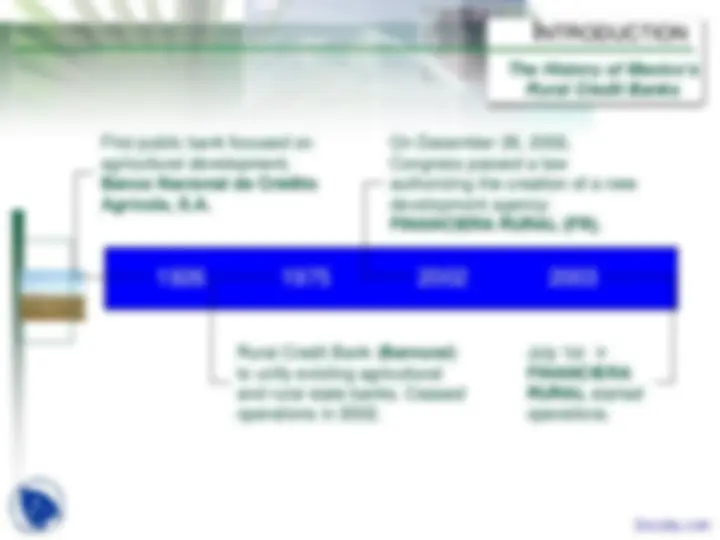
Development bank focused on agricultural activities
Funding through “unlimited” access to loans from the Federal Government
Operated as a subsity manager, with a high ratio of non- performing loans
Inefficient cost structure; operating costs over 100% of operating income
Defficient risk management
New Development Agency focused on rural productive projects
Legally banned from taking deposits, loans or market funding. Must maintain endowment value over time to sustain operations
Operates with credit processes that apply international best practices. Has spread payment culture among clients
Efficient cost structure
Best risk management practices
Banrural (^) Financiera Rural
C OMPARATIVE A NALYSIS
Financiera Rural vs. Banrural
[1] Even thouth currently Financiera Rural operates in the first tier, as well as the second, in the long term it expects to serve only as a second-tier lending institution.
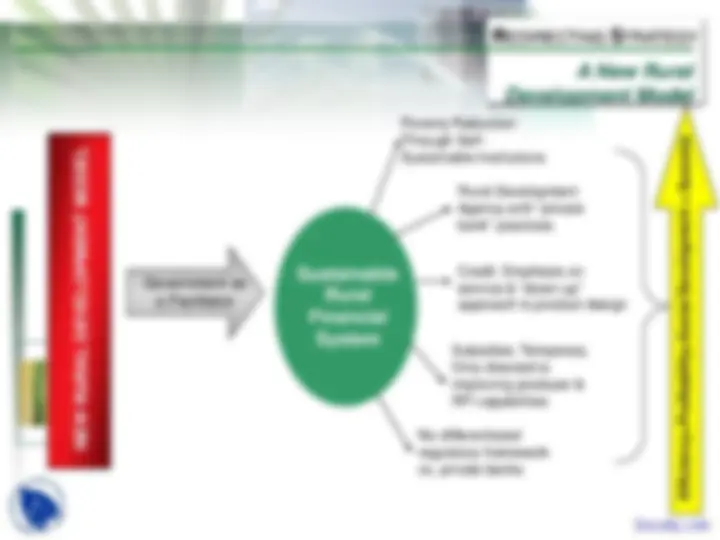
RURAL DEVELOPMENT AGENCY
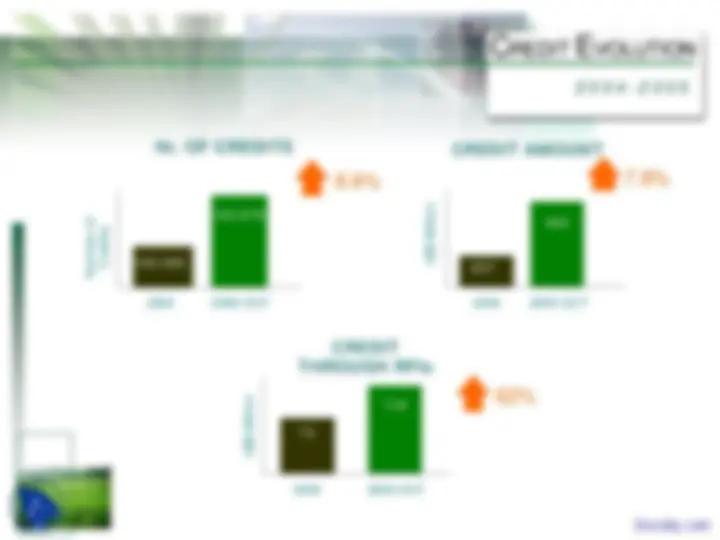
Initial Endowment of USD 1.72 billion** USD 1,534 Mill. Credit*
USD 79 Mill. pre-operating expenses
USD 49 Mill. Technical Assistance
Supervised Rural Financial Intermediaries
Informal Rural Credit Institutions
Individual Rural Producers
Technical assistance for credit enhancement and the creation of RFIs
Credit
*Of the initial USD 1.6 billion, USD 46 million could be used for the acquisition of Banrural assets (other than loans). ** Provided by Congress.
Rural Financial Intermediaries
*Governed by the new law for popular savings and loans ( Ley de Ahorro y Crédito Popular )
Other Organizations
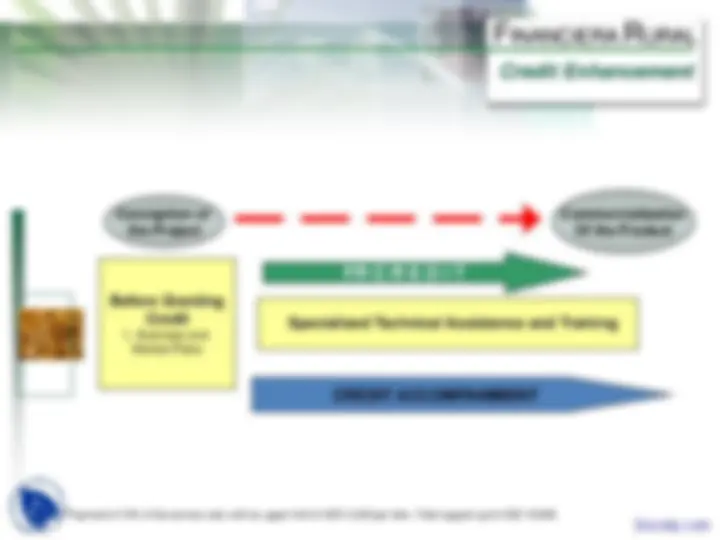
Conception of the Project
Commercialization Of the Product
Before Granting Credit
Specialized Technical Assistance and Training
Establishment
Sustainable Development
Individual Producers
Unsupervised Credit Organizations
Supervised Rural Financial A (^) Intermediaries Z
FR’s Credit and Technical Assistance to Develop Institutional Capabilities