







































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
During the course of work of the microprogramming, we learn the core of the programming. The main points disucss in these lecture slides are:External Memory, Types of External Memory, Magnetic Tape, Read and Write Mechanisms, Inductive Write, Data Organization and Formatting, Disk Data Layout, Disk Velocity, Constant Angular Velocity, Layout Methods
Typology: Slides
1 / 47

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!








































Chapter 6
External Memory
Types of External Memory
Read and Write Mechanisms
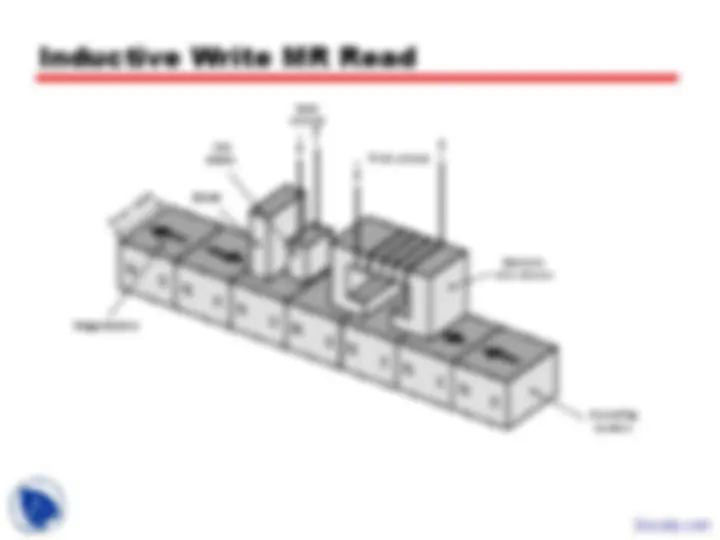
Inductive Write MR Read
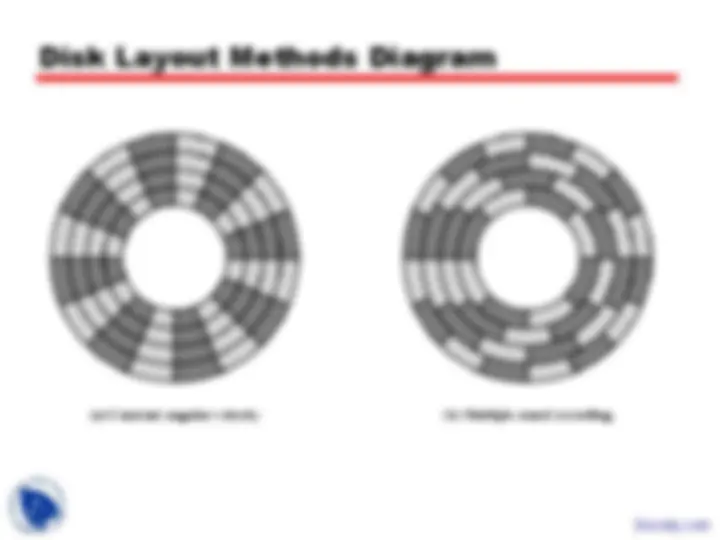
Disk Data Layout
Disk Velocity
Finding Sectors
Gap1 Id Gap2 Data Gap3 Gap1 Id Gap2 Data Gap
Track
Sync Byte Head^ Sector^ CRC^
Sync Byte Data CRC
ST506 format (old!)
Fixed/Movable Head Disk
Removable or Not
Multiple Platters
Cylinders
Winchester Hard Disk (1)
Winchester Hard Disk (2)