









Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
EXSC520 CASE STUDY 1 – CORRELATION AND BIVARIATE REGRESSION TEMPLATE
Typology: Assignments
1 / 17

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










Instructions: To successfully complete this case study, all of the following instructions must be adhered to. Only paste tables/figures that contain pertinent information. Only paste tables/ figures where you are instructed to do so. Highlight (in yellow) only relevant data from tables; as well as your response to each question. In the write-up section, all information must be provided in paragraph format. When statistical values are discussed, the numerical value must be given and a reference must be made to the table(s)/figure(s) where the value(s) can be found. An example of this is “heart rate was statistically greater during running versus cycling (189 vs. 143 bpm) as indicated in Table 1.” I. Correlation Research question: “ Is mean heart rate during exercise correlated to body weight? ” Assumptions Testing
Upper Bound
5% Trimmed Mean 132. Median 134. Variance 254. Std. Deviation 15. Minimum 108 Maximum 160 Range 52 Interquartile Range 29 Skewness .015.
Kurtosis -.639 1. Body_weight_Kg Mean 85.391 4. 95% Confidence Interval for Mean Lower Bound
Upper Bound
5% Trimmed Mean 84. Median 80. Variance 194. Std. Deviation 13. Minimum 73. Maximum 120. Range 46. Interquartile Range 9. Skewness 1.987. Kurtosis 3.797 1.
3. Was the assumption of normality met and how do you know? For mean heart rate yes, because sig is greater than .05 - .842. Body weight no, it is smaller than .05 - .002. Table 2. Tests of normality Paste table below: Tests of Normality Kolmogorov-Smirnova^ Shapiro-Wilk Statistic df Sig. Statistic df Sig. Mean_heart_rate_ BPM
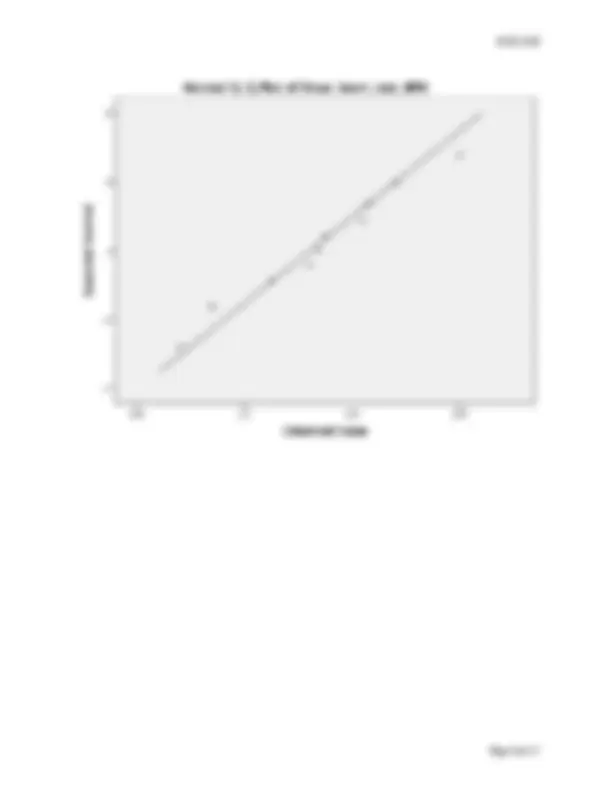
Figure 2. Normal Q-Q plot for each variable Paste figure below:
Statistical Analysis Table 4. Descriptives statistics table Paste table below: Descriptive Statistics Mean Std. Deviation N Mean_heart_rate_ BPM
Body_weight_Kg 85.391 13.9322 11
results that is not the case. This can be used practically to help determine why some people have a higher heart rate than others and how those with higher heart rates can potentially lower theirs. II. Bivariate Regression Research question: “ What is the relationship between mean heart rate and body weight?” Assumptions Testing
**Table 1. Table with skewness and kurtosis** Paste table below: 3. Was the assumption of normality met and how do you know? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Table 2. Tests of normality Paste table below:
Figure 1. Histogram with normal curve for each variable Paste figure below: Figure 2. Normal Q-Q plot for each variable Paste figure below:
**Table 3. Box-and-Whiskers plot for each variable** Paste table below: Statistical Analysis Table 4. Descriptives statistics table Paste table below: Descriptive Statistics Mean Std. Deviation N Mean_heart_rate_ BPM
Body_weight_Kg 85.391 13.9322 11 Table 5. Correlations table Paste table below: Correlations Mean_heart rate_BPM Body_weigh t_Kg Pearson Correlation Mean_heart_rate BPM
Body_weight_Kg -.705 1. Sig. (1-tailed) Mean_heart_rate_ BPM
Body_weight_Kg..
Table 8. The coefficients table Use this table to type out the regression equation for this data. Paste table below: Coefficientsa Model Unstandardized Coefficients Standardized Coefficientst Sig. 95.0% Confidence Interval for B Collinearity Statistics B Std. Error Beta Lower Bound Upper Bound Tolerance VIF 1 (Constant) 201.264 23.384 8.607. 148.366 254. Body_weight_Kg -.808 .271 -.705 -2.986. -1.420 -.196 1.000 1. a. Dependent Variable: Mean_heart_rate_BPM Coefficientsa Model Unstandardized Coefficients Standardized Coefficients t Sig. 95.0% Co B Std. Error Beta Lower Bou 1 (Constant) 201.264 23.384 8.607 .000 148. Body_weight_K g
a. Dependent Variable: Mean_heart_rate_BPM Y= a + bX Y= 201.264+-.
Write-up (8 sentence maximum) Include the following items: