



Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
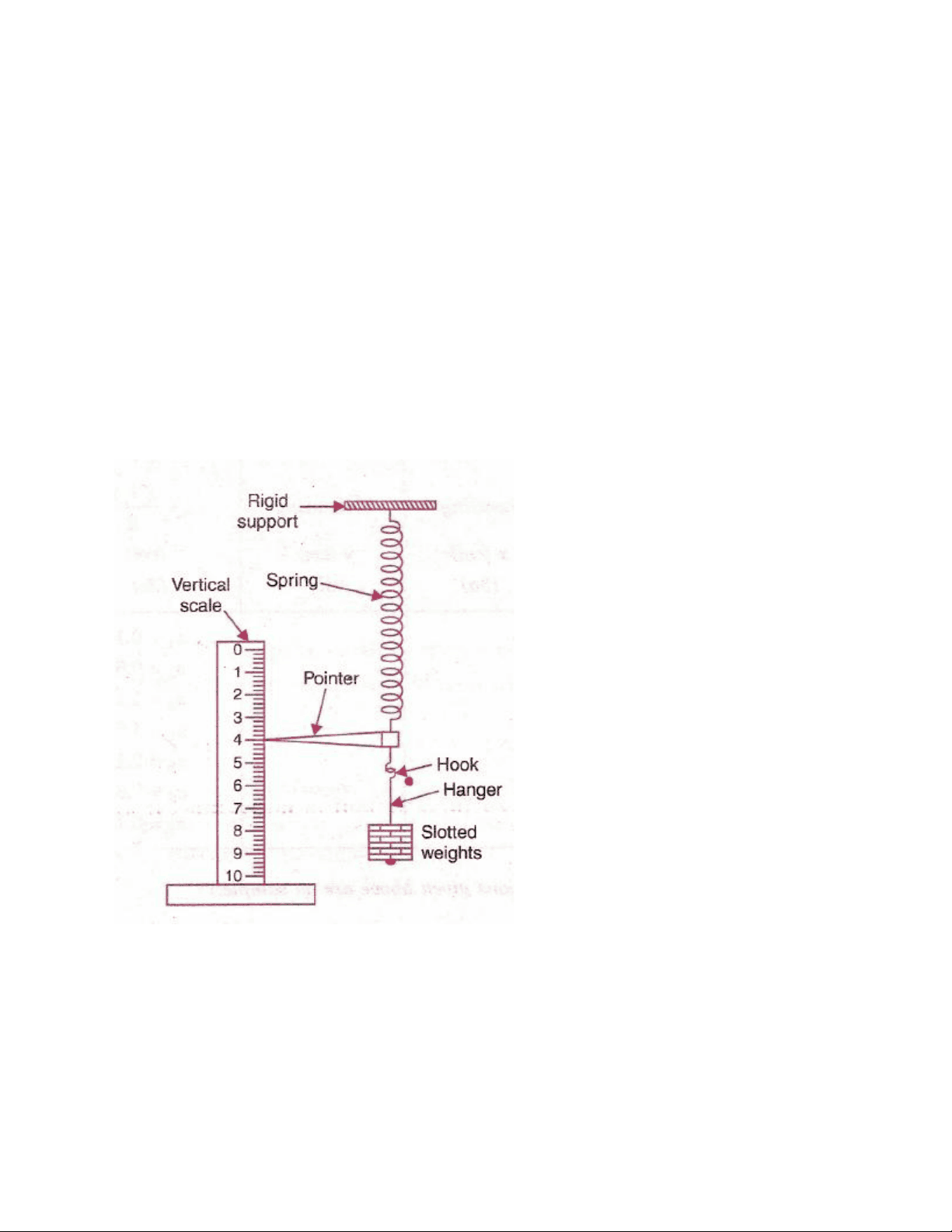
It is called the force constant or the spring constant of the spring. 1. Suspend the spring from a rigid support.
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 4

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



To find the force constant of a helical spring by plotting graph between load and extension.
APPARATUS Spring, a rigid support, slotted weights, a vertical wooden scale, a fine pointer, a hook. THEORY When a load F suspended from lower free end of a spring hanging from a rigid support, it increases its length by amount x,
or F= k x, where k i s constant of proportionality. It is called the force constant or the spring constant of the spring.
From graph, k =……………… gwt per cm.
The force constant of the given spring is …………. g wt per cm. PRECAUTIONS
Serial No.
Load (g) Reading of the scale while
Extension x (cm) Loading unloading