







Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An overview of exoplanet detection methods, including the transit method, radial velocity wobble, and direct observation infrared. It also discusses the kepler mission and its goal to determine the statistical probability of earth-like planets in our galaxy. The document also touches on the search for habitable planets in the milky way and the role of black holes in galaxy structures.
Typology: Slides
1 / 11

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!







1
Gravitational attraction between a stellar mass (sun) and planets (bigger the better, why?) makes sun’s position wobble about barycenter.
Big question is: How many planets are in life- zone where liquid water is stable?
Life zone is where a sun’s luminosity and a planet’s orbital radius are correct: the green zone below. The red zone is too hot (Mercury- like) and the blue zone is to cold and makes gaseous planets (Jupiter-like)
2 detected exoplanets to scale for planet orbital radius (planets not to scale!)
Our solar system to scale for Jupiter and Saturn orbital radius
2
Transit method: light dims
Radial velocity wobble (Doppler shift)
Direct observation infrared
4
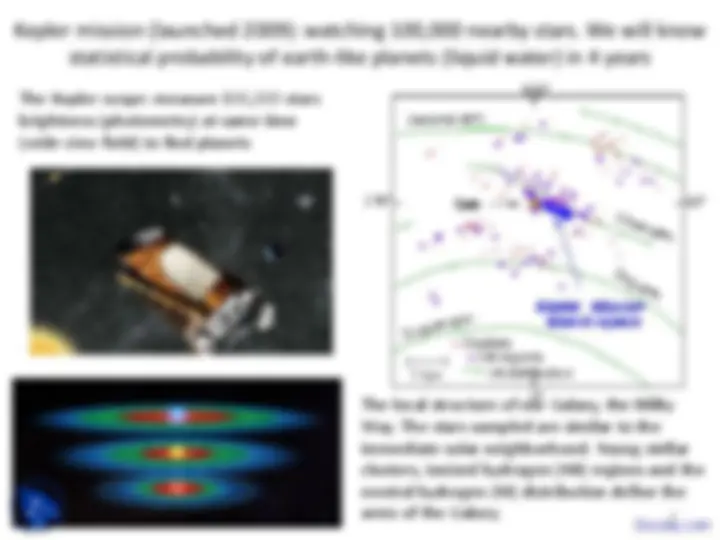
The Kepler-scope: measure 100,000 stars brightness (photometry) at same time (wide view field) to find planets
The local structure of our Galaxy, the Milky Way. The stars sampled are similar to the immediate solar neighborhood. Young stellar clusters, ionized hydrogen (HII) regions and the neutral hydrogen (HI) distribution define the arms of the Galaxy.
5
7
8
Galactic core black-hole sun motion for 8 yrs
10
Gravity is a busy force moving stuff around rapidly
Supermassive black holes at center of most all galaxies
11
Milky way galaxy center
Andromeda central SM blackhole