




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
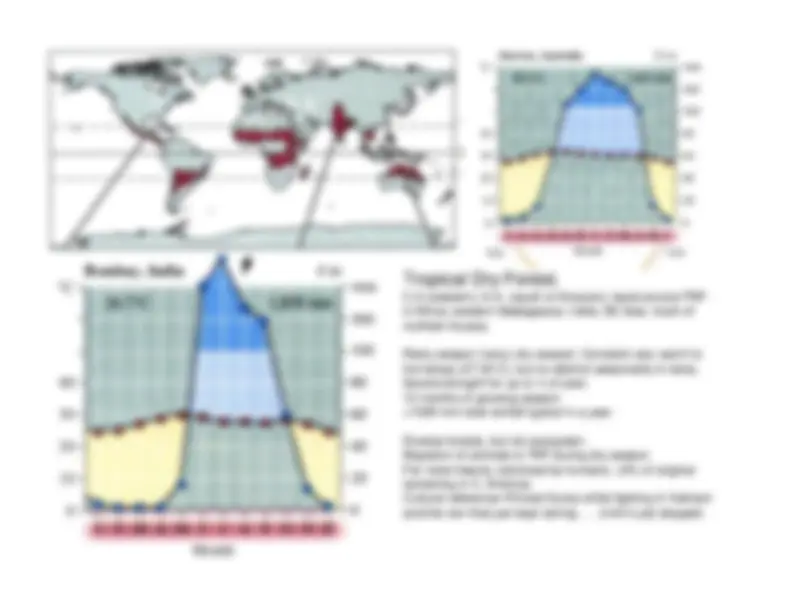
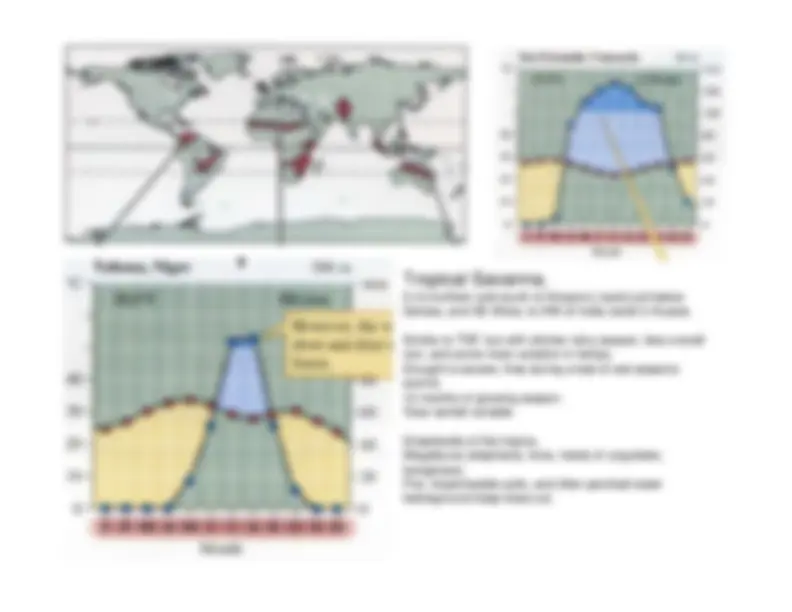
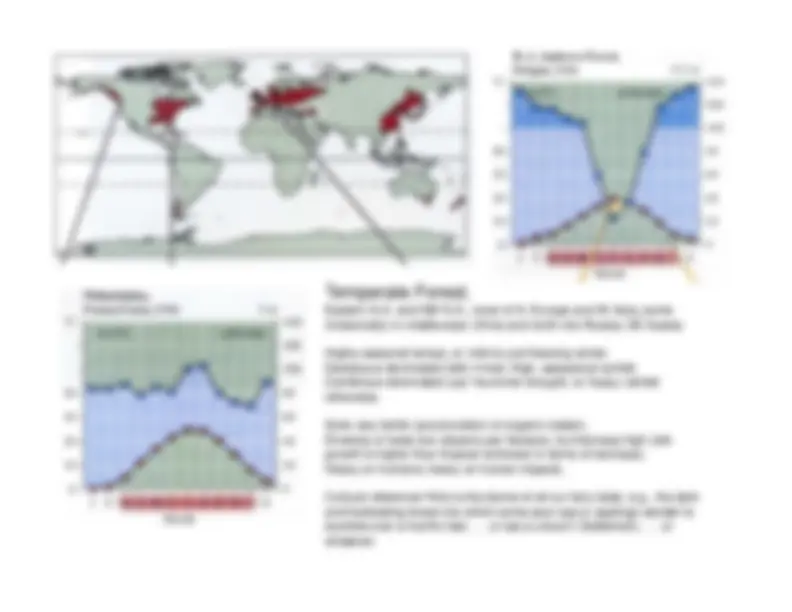
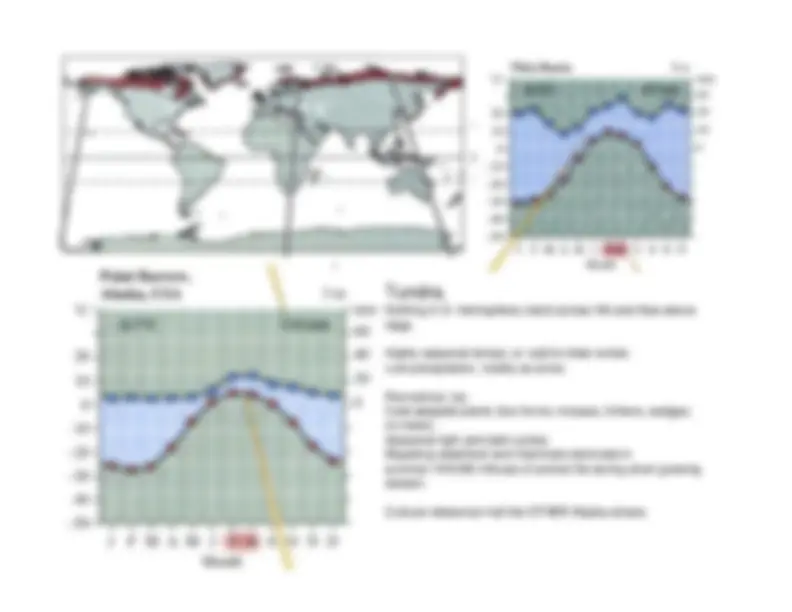
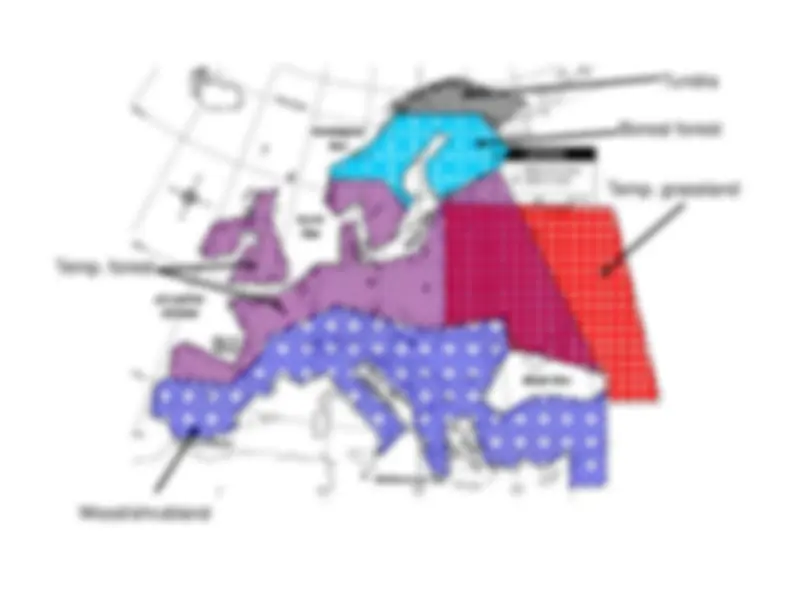
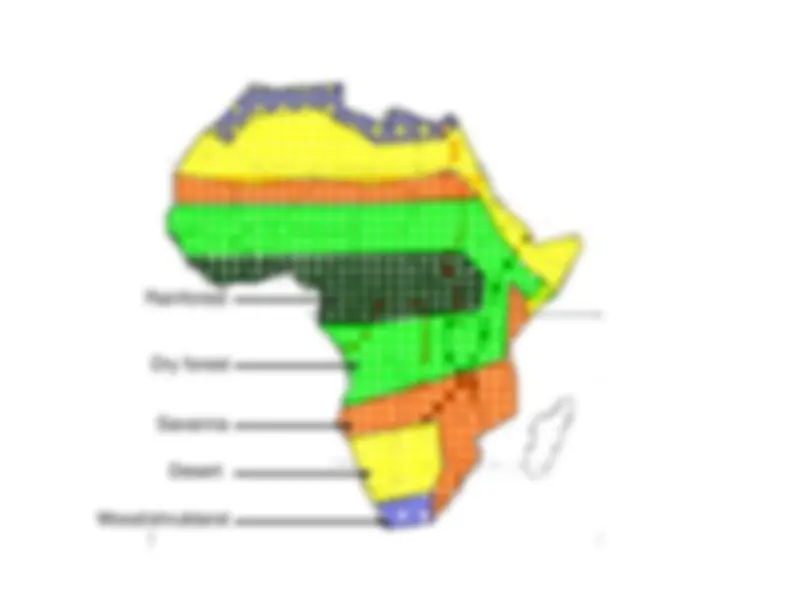
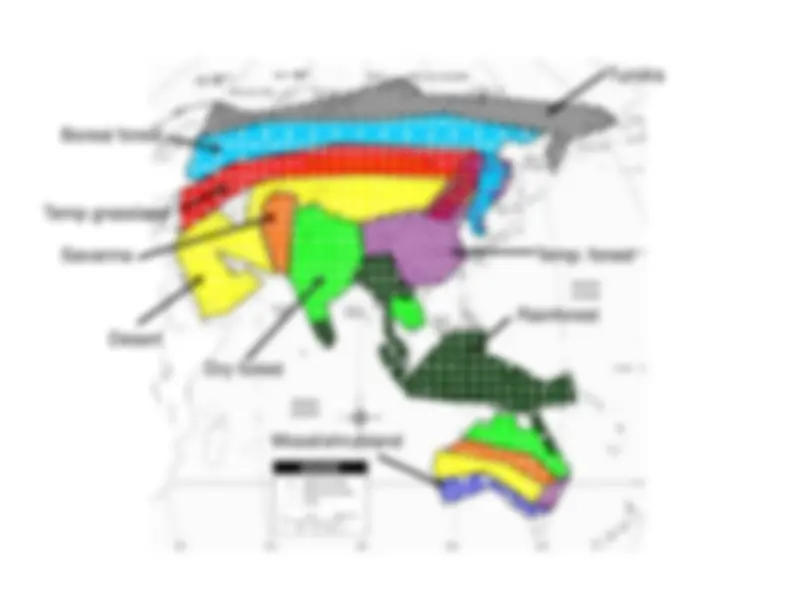
Detailed information about various climate diagrams and the characteristics of different biomes, including Tropical Rainforest, Tropical Dry Forest, Tropical Savanna, Temperate Woodland/Shrubland, Temperate Forest, Boreal Forest (Taiga), and Tundra. Each section includes the location, average temperature, precipitation, growing season, and distinctive features of the respective biome.
What you will learn
Typology: Study Guides, Projects, Research
1 / 15

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










minimum to
maintain non-drought conditions.Red is for temp; blue is for precip
if red
above blue, then drought; if blue above red,then non-drought.Months on x-axis: red highlighting indicatesgrowing season (ave temp > 0C).Year average temp (upper left) and totalrainfall (upper right).Location in far upper left; elevation far upperright.
distinct 3-D ecosystem. High decomposition rate in forest floor.Soils leached of nutrients and carbon; most tied up in trees.Very high biodiversity.
mod. High, aseasonal rainfall. Coniferous-dominated (up)
summer drought, w/ heavy rainfall otherwise.Soils very fertile (accumulation of organic matter).Diversity of trees low (dozens per hectare), but biomass high (old-growth is higher than tropical rainforest in terms of biomass).Heavy on humans; heavy on human impacts.Cultural reference
this is the biome of all our fairy tales, e.g., the dark and foreboding forest into which some poor sap or saplings wander tostumble over a horrific fate... or eat a unicorn (Voldemort)... orwhatever.
HUGE influxes of animal life during short growing season.Cultural reference
all the OTHER Alaska shows.