
















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This lecture belongs to lecture series on Health. Almost all topics related to health are covered in this course. Key points in this lecture are: Epidemiological Risk, Assessment Management, Effective Strategy, Forecasting and Management, Creation of Information Computer System, Epidemiological Risk Assessment, Chernobyl Disaster, Theory of Probability, Control System Intensities, Epidemilogical Risk
Typology: Slides
1 / 23

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
















On the other side the Chernobyl disasterand events of September 11, 2001 haveshown that even negligible value of riskcan occur. In this connection widespreadgets understanding that the unique andsingle character of so sophisticatedsubject as epidemic, and especially globalepidemics does not allow in some cases touse correctly the theory of probability forrisk assessment.
There is another approach to risk assessment,which may prove more useful here. In thisapproach the risk estimation is carried out usingthe theory of smooth functions allowing thedetermination of critical parameter values whichdescribe the levels of control system intensitiesand reserve possibilities. The risk is estimated ona degree of the system parameter approximationof the bifurcation values, which characterise thesystem’s transition from one steady state (norm),to another (catastrophe/epidemic).
Optimization problems were solved by a methodof casual search. The multicriterion statements of aproblem were considered, to find an optimumcontrol, which would permit to maximize the levelof manufacture and quality of life, on the onehand, and minimize epidemiological risk ofaccidents and level of pollution, on the other. Thiswork also illustrates the above approachapplication to HIV/AIDS risk assessment fordifferent countries using new WHO’s data
Main postulates
. Let us introduce some postulates that we
take as a basis of model elaboration.1.Epidemiological system is aggregate of elements thatcharacterize different aspects of infectious diseases arisingand spreading. Some of these elements belong to anothersystems – ecological, biomedical, and social.2. Epidemiological system has
three steady states
. Using
Guastello [5] idea about organization safety of complicatedsystems
it
is
possible
to
put
forward
a
following
suppositions.
The first
state is characterized by existence of
external
and
internal
safety
(
norm
).
Second
state
is
characterized by only external safety, as internal one isbroken (intermediate state or
preepidemic
).
Third
state
is
characterized by full loss of any safety, as external, sointernal (
epidemic
).
The
mathematical
model
for
epidemiological
risk assessment
The relationship between epidemic safety (X)and above-mentioned parameters aredetermined for butterfly catastropheby following polynomial :
X5 + aX3 + bX2 + cX + d = 0
On
the
base
of
works
dealing
with
methods
of
catastrophes
theory
a
following
algorithm
of
epidemiological risk assessment can be suggested.
Information
characterizing
agents
of
diseases,
population immune status and restoration possibilities,health
care,
environment
impacts
is
inputted
from
modern health care systems (EPID Info 2000, etc).
are
estimated
by
means
of
developed
mathematical models with the help of inputted data.
Forecasting of infectious diseases arising andspreading.Optimization problems of risk management.
The mathematical model was used to solve some problems of optimum redistribution of resources
with the purpose of minimization of epidemic risklevel and pollution and maximization of lifequality and GNP. The shares of the capital,directed on restoration of resources, on health careand on struggle with pollution were chosen ascontrol parameters..
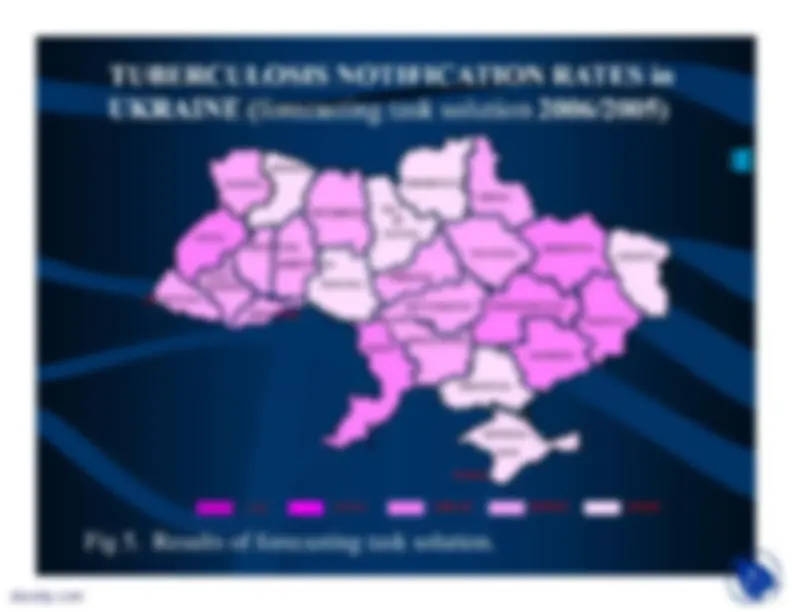
Optimization task solution and risk assessment
On
Figure 3
the modeling results are shown,
which reflect dynamics of main model variableswith fixed control effects, and with control effectsvarying in the course of time, and also thedynamics of control effects.
Analysis of WHO date on HIV/AIDS risk assessment for different countries
Examine the example of above approach application to HIV/AIDS escalation riskassessment. The WHO data for differentcountries presented at Table 1 wereutilized.