






Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Embryology is a branch of science that is related to the formation, growth, and development of embryo. It deals with the prenatal stage of development beginning from formation of gametes, fertilization, formation of zygote, development of embryo and fetus to the birth of a new individual.
Typology: Study Guides, Projects, Research
1 / 16

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










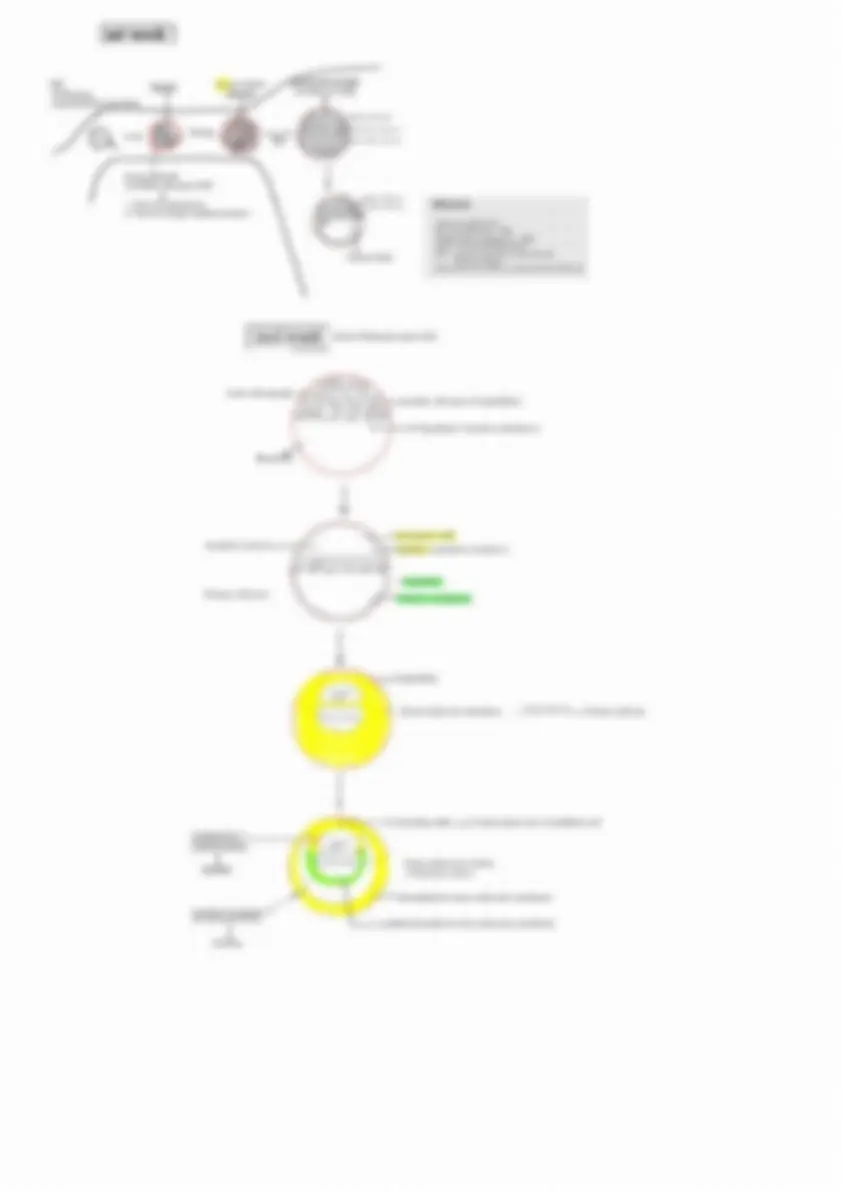
Epiblast
2nd week
Primordial germ cells ( PGC )
Migrate to
Wall of yolk sac
5th week ( PGC again migrate )
Genital ridge ( Testies/ ovary )
PGC Gametogonium Spermatogenesis
Oogenesis
Spermatogonium
Mitotic division
Primary spermatocyte ( 2n )
Meiosis I
Secondary spermatocyte
Sertoli cells (^) Meiosis II
Spermatid
Spermiogenesis
Tight junction (Zona occludens)
Blood testies barrier
Spermatozoa
Spermiation
Release of spermatozoa in the lumen of seminiferous tubule
Epididymis Storage Maturation Motility
Final stage of maturation is also known as capacitation which takes place in female genital tract ( Isthmus of Fallopian tube )
Site for spermatogenesis = Seminiferous tubule
Time take = 72-74 days
1 spermatogonium = 64-512 spermatids
Oogonium
Before birth
Primary oocyst (2n)
Meiosis I
Arrested in Prophase I ( Diplotene )
Childhood
Puberty
Ovaries are inactive
LH surge (~36 days prior to ovulation )
Meiosis I completes
Secondary oocyte + 1st polar body (n)
Meiosis II
Arrested in metaphase II
Meiosis II is complete only if fertilisation takes place
Head end of embryo
Prochordal plate
Week of gastrulation
Tail end of embryo
Epiblast
Hypoblast
Notochord is the first structure defining craniocaudal axis of the embryo
Primitive knot ( Hensen’s node ) Primitive streak
Head Tail
Will give rose to all 3 germ layers
Prochordal plate ( future buccopharyngeal membrane )
Notochord Ectoderm + endoderm Proliferative mesoderm Primitive Knot
Primitive Ectoderm + Endoderm Streak Cloacal membrane
Tail
Neural crest cells
Neural fold
Neural groove Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Notochord Endoderm
Neural crest cells
Neural Somatopleuric lateral plate mesoderm Tube Intra embryonic coelom
Splanchnopleuric lateral plate mesoderm
Para-axial mesoderm Somites
Notochord
Intermediate mesoderm Urogenital system
Lateral plate mesoderm Somatopleuric lateral plate mesoderm
Splanchnopleuric lateral plate mesoderm
Somites
Neural tube
Para-axial mesoderm
D20-D30 = Somite period
Primitive somites = 42-44 pairs
Somites
Occipital somites — 4 Cervical somites — 8 Thoracic somites — 12 Lumbar somites — 5 Sacral somites — 5 Coccygeal somites — 8-
Definative somites = 36-38 pairs
Dermatome
Dermis of back
Sclerotome (^) Myotome ( Skeletal muscle )
Axial skeleton, Ribs, vertebrae & Annulus fibrosus ( intervertebral disc )
Epiaxial myotome
— Erector spinal — Multifidus
Hypoaxial myotome
— Limb muscle — Abdominal muscle — intercostal muscle
Lateral plate mesoderm
Somatopleuric lateral plate mesoderm
Splanchnopleuric lateral plate mesoderm
Ectoderm
Endoderm
Peritoneal cavity
Intra embryonic coelom (^) Pleural cavity
Pericardial cavity
Somatopleuric lateral plate mesoderm
Splanchnopleuric lateral plate mesoderm
Derivatives of septum transversum
Buccopharyngeal membrane
Septum Transversum
Undifferentiated lateral plate mesoderm at the cranial end Most cranial structure before folding
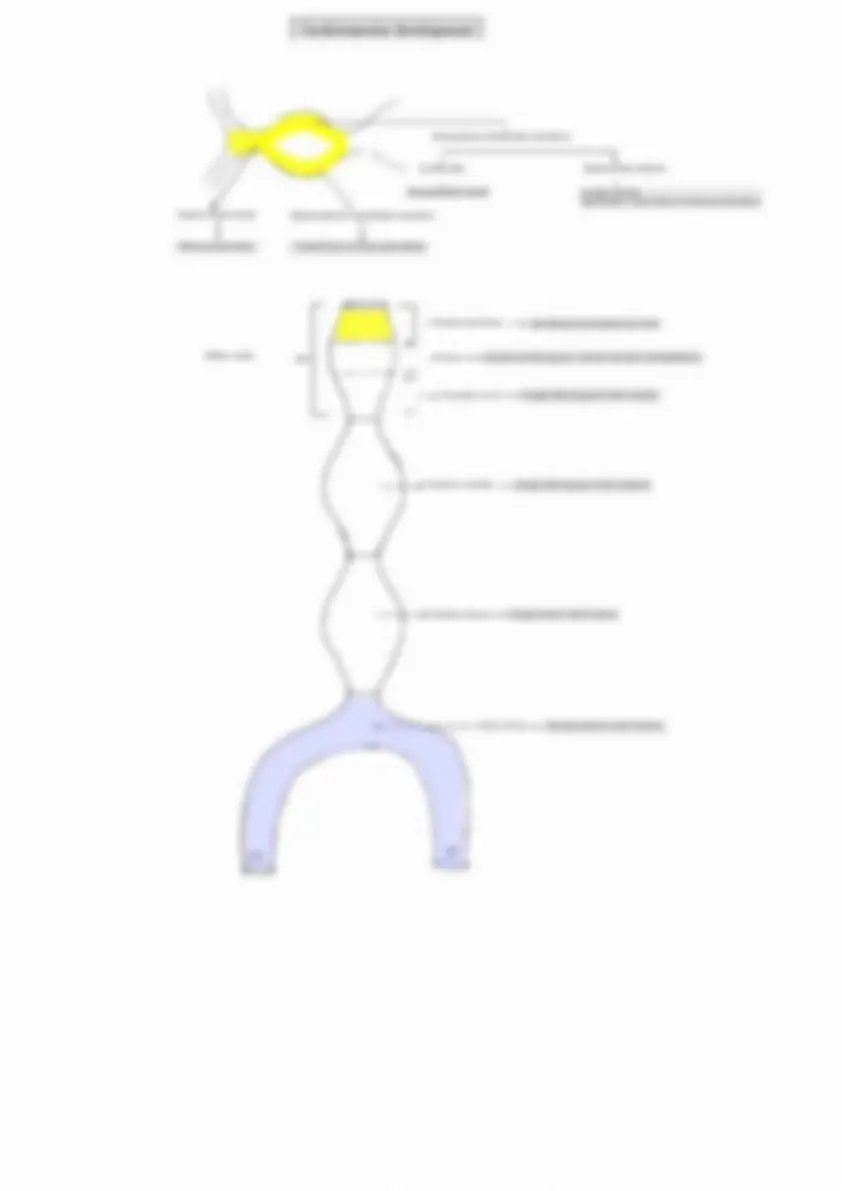
Arches Nerves
I Mandibular & chorda tympani
Muscles
Muscles of mastication, TVP, TT, Mylohyoid, Anterior belly of digastric
Arteries
Maxillary artery
II Facial nerve
III Glossopharyngeal nerve
IV Superior laryngeal nerve
VI Recurrent laryngeal nerve
Facial muscles, stapedius, posterior belly of digastric, stylohyoid, Auricular muscle & occipitalis
Stylopharyngeus
Cricothyroid + muscles of palate (except TVP) + muscles of pharynx (except Stylopharyngeus & Cricopharyngeus )
Cricopharyngeus, muscles of larynx (except Cricothyroid)
Stapedial & Hyoid artery
Common carotid & internal carotid artery
Arch of aorta + Right subclavian artery
Pulmonary artery + ductus arteriosus
Frontonasal process
Nasal pits Medial nasal process Lateral nasal process
Maxillary process
Mandibular process
Lower lip — derived from Mandibular process only Upper lip — derived from maxillary process + medial nasal process
Philtrum
Non fusion of medial nasal process —midline cleft upper lip Non fusion of maxillary process & medial nasal process — unilateral cleft upper lip Oblique facial cleft ( nasolacrimal duct is exposed ) — Non fusion of maxillary process to lateral nasal process
Ala — Lateral nasal palate
Palate — medial nasal process & maxillary process
Incisive part
Derivatives of medial nasal process — Tip of nose Anterior part of nasal septum Columella Philtrum Incisive part of palate
Tuberculum impart Lingual swelling
I
II (^) Hypobranchial eminence
III Copula
IV Epiglottis
VI
Tongue muscles are derived from occipital somites (GSE ) except Palatoglossus ( IV arch )
Lining epithelial of anterior 2/3rd of tongue = ectoderm
Limb epithelial of posterior 1/3rd of tongue = endoderm
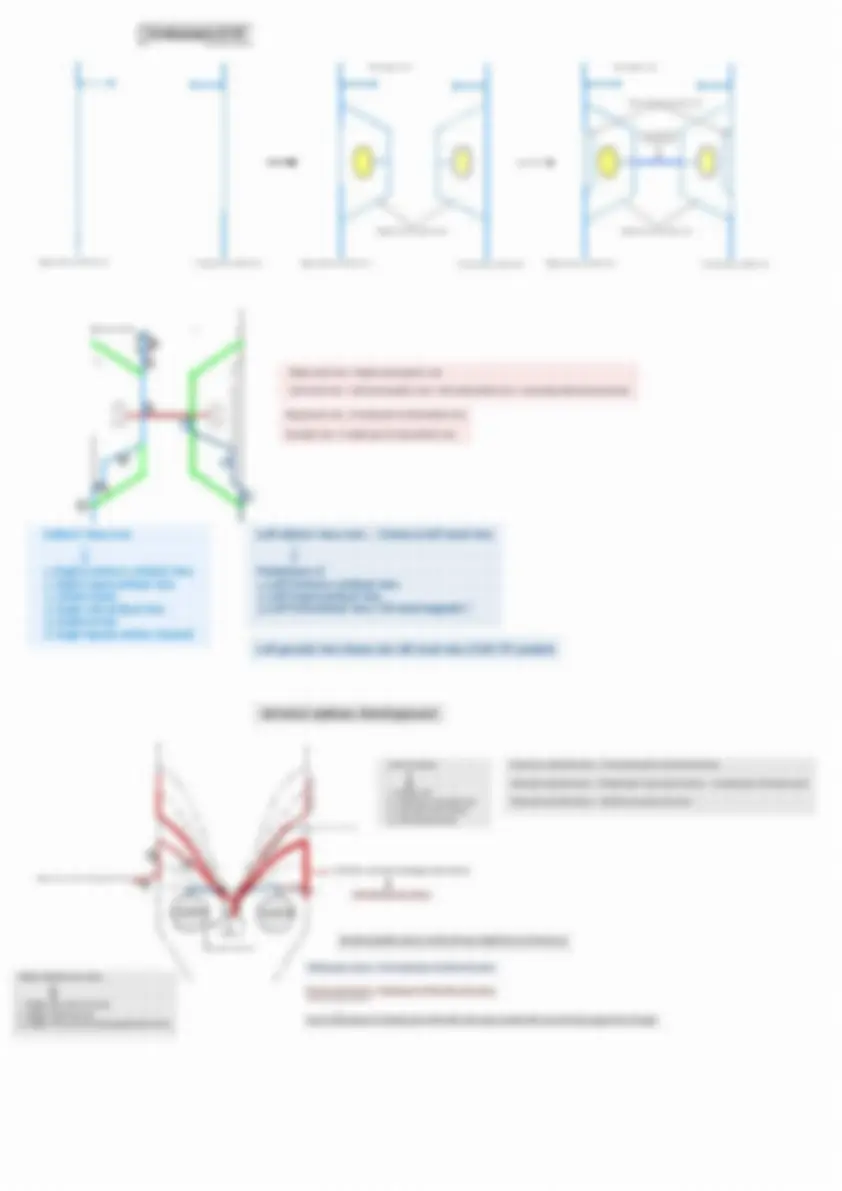
Cardiovascular development
Somatopleuric lateral plate mesoderm
Septum Transversum
Fibrous pericardium
Cardiac jelly
Myoepicardial mantle
Splancnopleuric lateral plate mesoderm
Parietal layer of serous pericardium
Edndocardial cushions
Cardiac muscles Epicardium ( visceral layer of serous pericardium
Trunkus arteriosus (^) Ascending aorta & pulmonary trunk
Bulbos cordis (^) Conus Smooth out flowing part of both ventricles ( Infundibulum )
Proximal 1/3 rd
Primitive ventricle
Primitive atrium
Rough inflowing part of left ventricle
Rough inflowing part of left ventricle
Rough anterior wall of atrium
Sinus venous Smooth posterior wall of atrium
RH
LH
nte (^) n l ca (^) ot (^) d te y
Mesonephric vein Mesonephric vein
Right & left supracardinal vein
Intersubcardinal Anastomosis
Right & left subcardinal veins Right & left subcardinal veins
Right posterior cardinal vein (^) Left posterior cardinal vein Right posterior cardinal vein (^) Left posterior cardinal vein Right posterior cardinal vein (^) Left posterior cardinal vein
6
5 Right renal vein = Right mesonephric vein
Left renal vein = Left mesonephric vein + left subcardinal vein + intersubcardinal anastomosis
4 Suprarenal vein = Cranial part of subcardinal vein 3 Gonadal vein = Caudal part of subcardinal vein
(^3 )
2 1 1
Arter i al system development
Arch of aorta
Common carotid artery = Proximal part of 3rd arch artery
Internal carotid artery = Distal part of 3rd arch artery + cranial part of dorsal aorta
External carotid artery = Bud from 3rd arch artery
2
Right 7th cervical intersegmental artery 3
1
Lung bud
Left 7th cervical intersegmental artery
Left subclavian artery
Lung bud
Aortic sac Brachiocephalic artery is derived from Right horn of Aortic sac Trunkus arteriosus
Right subclavian artery
Pulmonary artery = Proximal part of 6th arch artery
Ductus arteriosus = Distal part of left 6th arch artery
Due to persistence of distal part of left 6th arch artery makes left recurrent laryngeal nerve longer
Right 7th cervical intersegmental artery
Abnormal right subclavian artery
Persistence of caudal part of Right dorsal aorta ( if left 4th arch artery is obliterated ) Caudal part of left descending aorta
Descending aorta
Obliteration of oesophagus Fused dorsal aortae
Dysphasia, lusoria
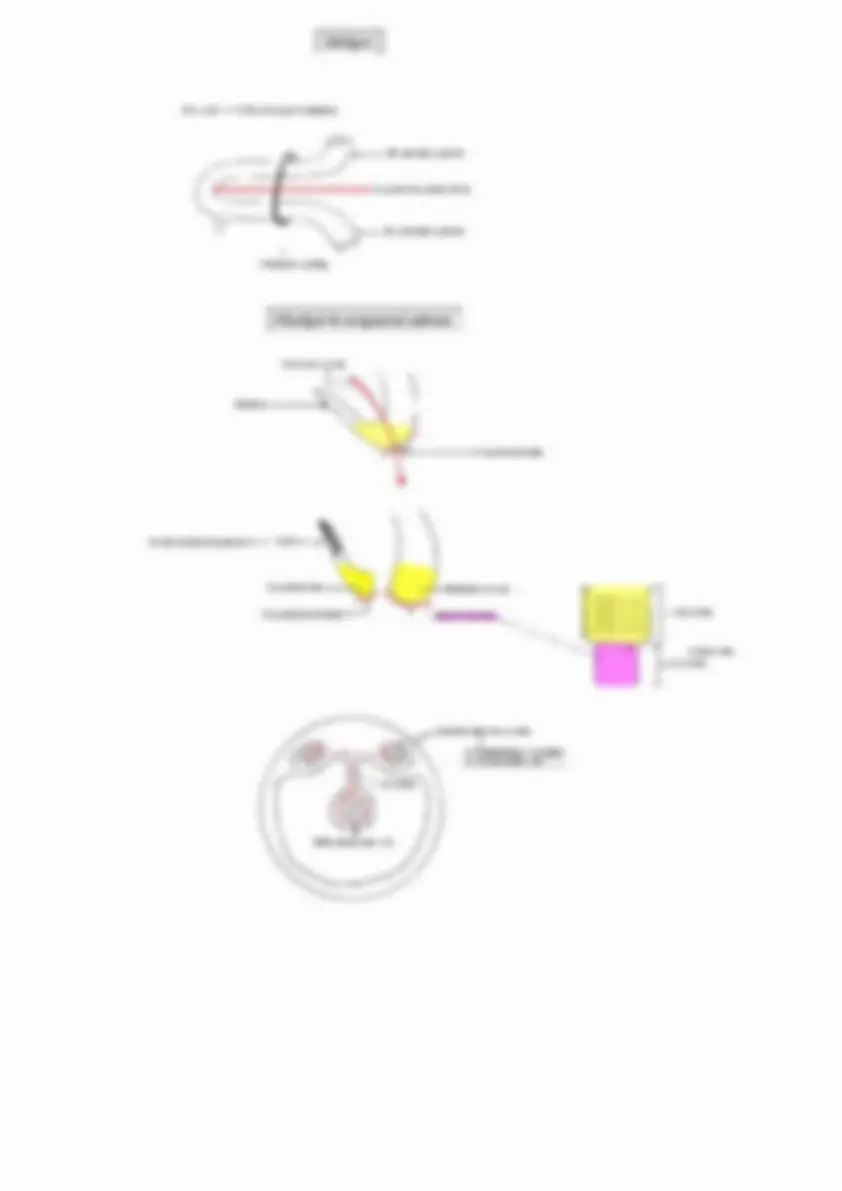
Interatri al septum
Septum secondum Gives rise to limbus or margin of fossa ovalis
RA LA Foramen ovale
Septum primum Gives rise to floor of fossa ovalis
Endocardial cushion
Usually due to non fusion of septum primum to endocardial cushion
Interventricular septum
Trunkus arteriosus Aorticopulmonary septum ( spiral septum )
Endocardial cushion
Bulbar septum Neural crest cells
Membranous part
Muscular part
Forgut
R espira tor y bud
H epa t i c bud
Ven t ra l pan cr ea t i c bud Dor sa l pan cr ea t i c bud
Septum t ran sv er sum ( m esode rm ) St r oma of the l iv er + Kupffe r cells
H epa t i c bud ( en dode rm ) H epa tocytes + bi l iary a ppara tus
Dor sa l pan cr ea t i c duct
Ven t ra l pan cr ea t i c duct
Do r sa l pan cr ea t i c bud
Ven t ra l pan cr ea t i c bud
Axia l rot a t i on due to di ffer en t ia l g rowth
Dor sa l pan cr ea t i c bud G iv es ri se to
Ven t ra l pan cr ea t i c bud G iv es ri se to
M ain pan cr ea t i c duct ( Duct of w irsu n g) = v en t ra l pan cr ea t i c duct + di st a l par t of dor sa l pan crea t i c duct
A ccesso r y pan cr ea t i c duct = p ro xima l part of dor sa l pan cr ea t i c duct
Mc dev elopm en t a l an oma ly of p an crea s — Pan cr ea t i c divi sum
Ven t ra l m esog a st ri um Septum t ran sv er sum
Sto ma ch 4. L^ esser^ om^ en^ tum^ H^ epa^ tog^ a^ st^ ri^ c^ l^ i^ g^ am^ en^ t H epa toduode na l l i g am en t
Dor sa l m esog a st ri um Spl an cn opleu ri c l a tera l pl a te m esode rm
Midgut
6 th week Physi olog i ca l hernia t i on
Pre arteria l segm en t
Supe ri or m esen t ri c artery
Post arteria l seg m en t
U m bi l i ca l openin g
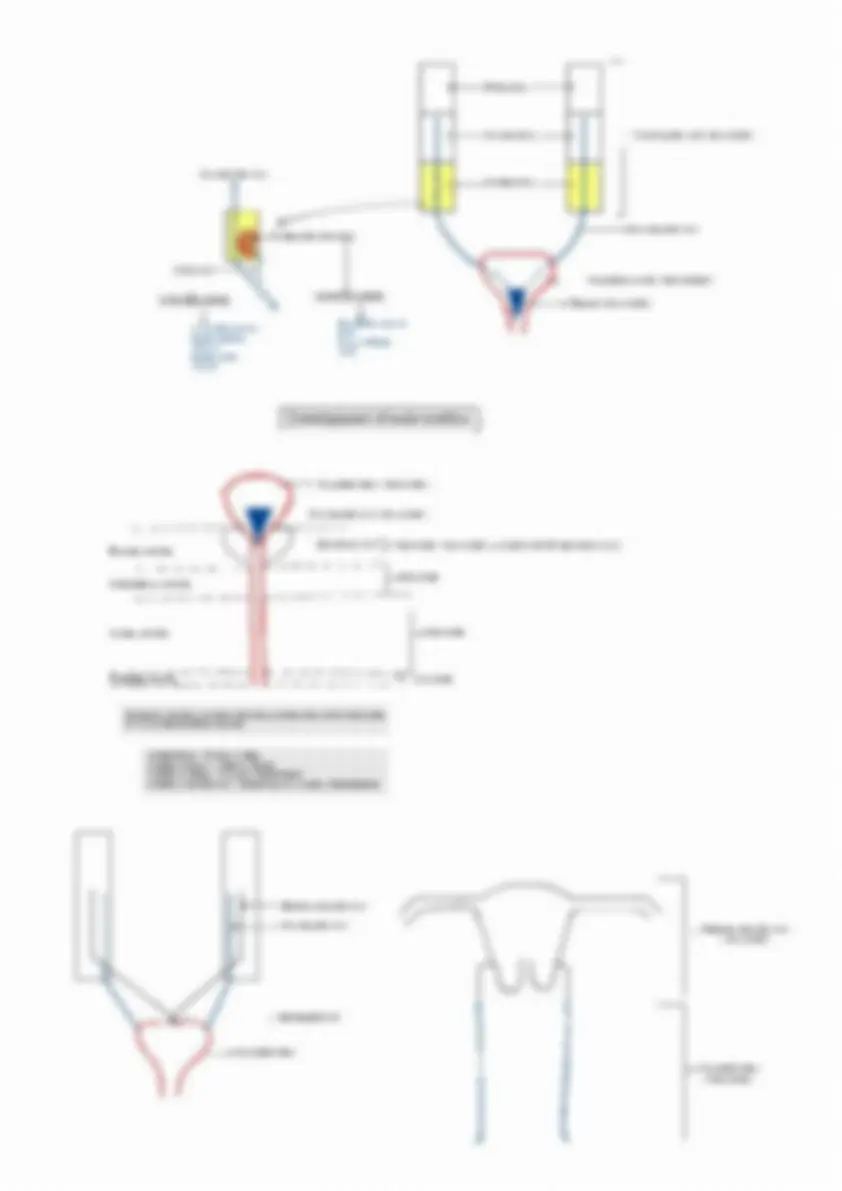
Hi ndgut & urogeni tal system
U r or ect a l septum
A ll an toi s
Clo a ca l m em bran e
Med ia l um bi l i ca l l i g am en t U^ ra^ chus
U r ogeni t a l sin us
U r ogeni t a l m em bran e
Primi t ive rectum
Ana l m em bran e E^ n^ dode^ rm
Den t a te l in e Ectode rm
In term edia te m esode rm
Mese n t ry
Yolk Sac
Prim ordia l ge rm cells
M a le
va s defe r en ce eja cul a tor y duct semina l vesi cle epi di dy mi s
Fema le
M a le
A ppen dix of T est i es Pr ost a t i c ut ri cles
Fema le
Fa llopian tube Uter us Uppe r part of va g ina