





Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
These are the Lecture Slides of Embedded System Design which includes Hardware Design, Elevator Controller, Simple Elevator Controller, Try Capturing, Unit Control, Request Resolver, Sequential Program Model, Partial English Description, System Interface etc. Key important points are: Development Environment , Processor, Programs, Target Processor, Compilers, Cross Compiler, Assemblers, Linkers, Debuggers, Profilers
Typology: Slides
1 / 15

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










Development processor Target processor
Instruction Set Simulator For A Simple
Processor
typedef struct { unsigned char first_byte, second_byte; } instruction;
instruction program[1024]; //instruction memory unsigned char memory[256]; //data memory
int run_program(int num_bytes) {
int pc = -1; unsigned char reg[16], fb, sb;
while( ++pc < (num_bytes / 2) ) { fb = program[pc].first_byte; sb = program[pc].second_byte; switch( fb >> 4 ) { case 0: reg[fb & 0x0f] = memory[sb]; break; case 1: memory[sb] = reg[fb & 0x0f]; break; case 2: memory[reg[fb & 0x0f]] = reg[sb >> 4]; break; case 3: reg[fb & 0x0f] = sb; break; case 4: reg[fb & 0x0f] += reg[sb >> 4]; break; case 5: reg[fb & 0x0f] -= reg[sb >> 4]; break; case 6: pc += sb; break; default: return – 1;
return 0; }
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
FILE* ifs;
If( argc != 2 || (ifs = fopen(argv[1], “rb”) == NULL ) { return – 1; } if (run_program(fread(ifs,program, sizeof(program)) == 0) { print_memory_contents(); return(0); } else return(-1); }
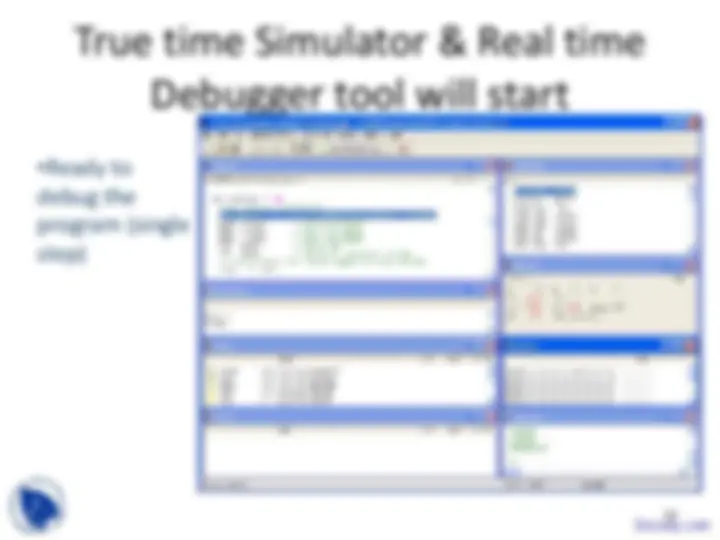
Verification Phase
Emulator
Development processor
(a) (b)
External tools
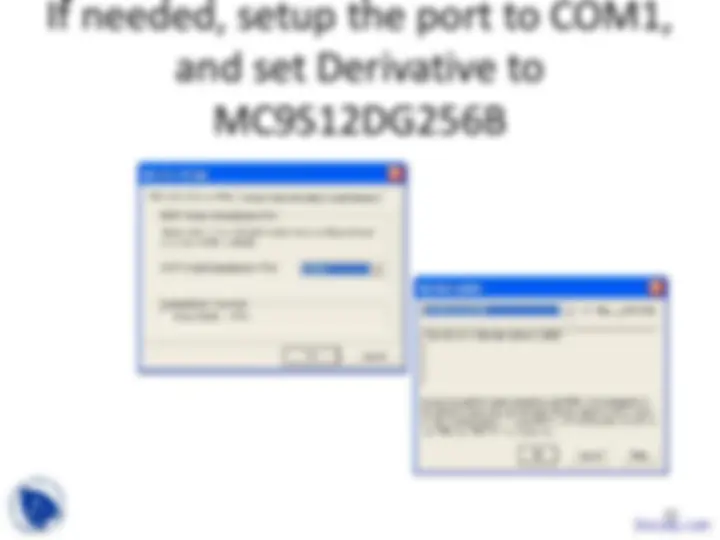
Change Full chip simulation to
HCS12 Serial Monitor