




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
The spring 2000 midterm 2 exam for the eecs 40 course at the university of california, berkeley. The exam covers various topics including circuits with dependent sources, transient response, op-amp circuits, and semiconductor properties. Students are required to solve problems related to nodal analysis, thevenin equivalent circuits, op-amp circuits, and p-n diodes.
Typology: Exams
1 / 5

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




a) Find V 0. [4 pts]
b) In the circuit below, the independent source values and resistances are known. Use the nodal analysis technique to write 3 equations sufficient to solve for Va, Vb, and Vc. To receive credit, you must write your answer in the box below. [6 pts]
Write the nodal equations here:
c) Consider the following circuit:
EECS 40, Spring 2000 Midterm 2 Professor King 1
i) Find the voltage Vab. [5 pts]
ii) What is the current ia when the terminals a and b are shorted together? [3pts]
iii) Draw the Thevenin Equivalent Circuit. [2pts]
a) In the circuit below, the switch has been in the closed position for a long time.
i) Find the value of vR just after the switch opens (t = 0+). [3 pts]
ii) How much energy is dissipated in the 1 k-ohm resistor after the switch is opened? [2 pts]
b) In the circuit below, the 5 micro-farad capacitor is initially charged to 5 V (vC1(0-) = 5 V). The switch is then closed at time t = 0. What is the final value of vC1? [5 pts]
c) The following is a circuit model for an NMOS inverter, in which the transistor is turned on at time t = 0:
Problem #1: Circuits with Dependent Sources [20 points] 2
Find Vout in terms of V1, V2, R1, R2, R3, F4. [10 pts]
(Hint: The superposition method might be helpful here.)
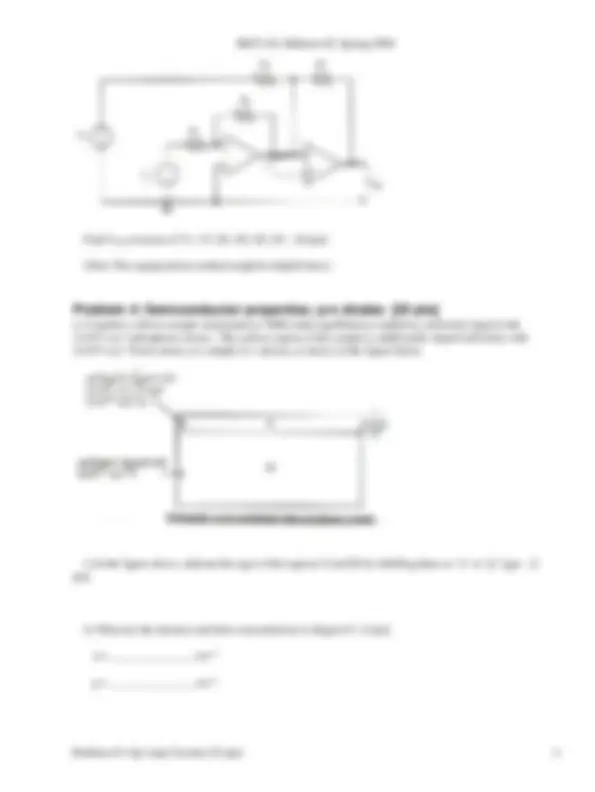
a) Consider a silicon sample maintained at 300K under equilibrium conditions, uniformly doped with 1x10^16 cm-3^ phosphorus atoms. The surface region of the sample is additionally doped uniformly with 5x10^16 cm-3^ boron atoms, to a depth of 1 micron, as shown in the figure below.
i) In the figure above, indicate the type of the regions (I and II) by labelling them as "n" or "p" type. [ pts]
ii) What are the electron and hole concentrations in Region I? [5 pts]
n = _______________ cm-
p = _______________ cm-
Problem #3: Op-Amp Circuits [25 pts] 4
iii) What is the sheet resistance of Region I? [5 pts]
iv) Suppose any voltage between 0 V and 5 V can be applied to Region I. What fixed voltage ("bias") would you apply to Region II, to guarantee that no current would ever flow between Region I and Region II? Briefly explain your answer. [3 pts]
b) If a diode is operated only within a small range of forward-bias voltages, its behavior can be accurately modelled by a resistor, whose value is dependent on the bias voltage. Device an expression for the diode "small-signal" resistance:
in terms of the saturation current Is, the bias voltage V, and the absolute temperature T. [5 pts]
Rdiode = ________________________
c) Plot vL vs. VIN for -10 V < VIN < 10 V on the axes provided, for the circuit below, Note that the diode is a perfect rectifier. Label the axes. [5 pts]
Problem 4: Semiconductor properties; p-n diodes [25 pts] 5