









Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Data Storage Concepts, Classification, Physical Storage Media, Speed of access, Cost per unit of data, Reliability, RAID, Multi Mirroring are the main points of this lecture.
Typology: Slides
1 / 14

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!









Statistics about the size and usage of data plays critical role in data processing efficiency Final step of logical DB design or first step in physical DB design
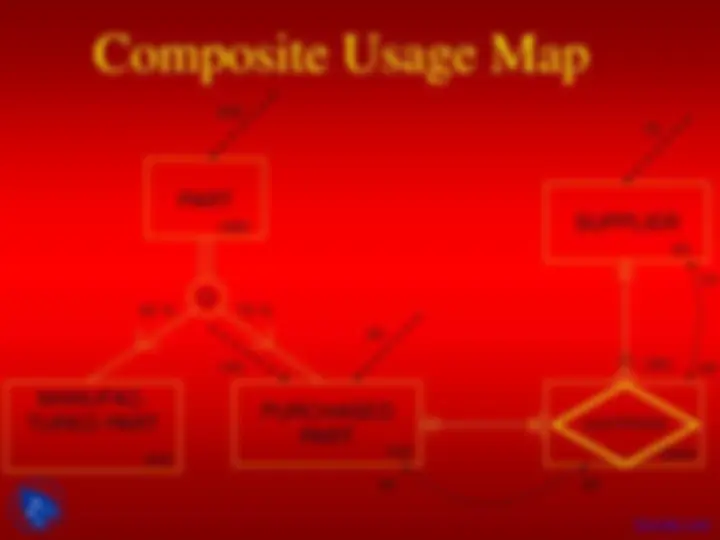
Composite Usage Map
PART 1000
TURED PART^ MANUFAC- PURCHASED PART
O
QUOTATION
SUPPLIER
2500
40 % 70 %
50
140
200
60
40 80
75
(50) (^40)
70
400 700
Choosing Data Type
Data type is defined as set of values along with the operations that can be performed on them
Precisely depends on the particular DBMS
Choosing Data Types
Involves four objectives
Coding Example stId stName hobby S1020 Sohail Dar Reading S1038 Shoaib Ali Gardening S1015 Tahira Ejaz Reading S1015 Tahira Ejaz Movies S1018 Arif Zia Reading
STUDENT
Coding Example
stId stName hobby S1020 Sohail Dar R S1038 Shoaib Ali G S1015 Tahira Ejaz R S1015 Tahira Ejaz M S1018 Arif Zia R
code Hobby R Reading G Gardening M Movies
STUDENT (^) HOBBY
Controlling Data Integrity
Default value Range control Null values Referential integrity Handling missing data