Download Understanding Vacuum Technology: Conductances, Pumpdown, Venting, Pressure Curves and more Slides Material Engineering in PDF only on Docsity!
Page 1
Vacuum Technology
Page 2
Conductances
- Series conductances
- Parallel conductances
C 1 C 2
1 2
CT C C
C 1
C 2
CT = C 1 + C 2
Page 3
Pumpdown Procedure
- 1.Start-up
- Turn on pumps
- Open foreline valve
- 2.Close foreline valve
- 3.Open roughing valve
- Rough chamber ~100mtorr
- 5.Close roughing valve
- 6.Open foreline valve
- 7.Open high-vac valve
Foreline Valve
High-Vac Pump
Chamber
Mechanical Pump
High-vac Valve Roughing valve
N 2
Vent valve
Vacuum Technology
Page 4
Venting Procedure
- 1.Close high-vac valve
- 2.Open vent valve
- Why N 2 or Ar for venting chamber??
Foreline Valve
High-Vac Pump
Chamber
Mechanical Pump
High-vac Valve Roughing valve
N 2
Vent valve
Page 7
System Pumpdown
Time (s)
Pressure (Pa)
100mTorr
Vacuum Technology
Page 8
System Pumpdown
- High Vac Pumping
- Use molecular flow equations
1
S (^) eff Sp HVP C
High-Vac Pump
Chamber
Mechanical Pump
High-vac Valve Roughing valve
N 2
Vent valve
C 1
C 2
C 3
1E-
1E-
1E-
1E-
10 0 5 10 15 20 25
Time (s)
Pressure (Torr)
Seff = 1m 3 /s
V=1m 3
Page 9
Real Systems
- Pressure limits in vacuum
systems
- 1st term -- time dependence of pressure that is due to the gas in the chamber volume (exp(-t))
- 2nd term -- pressure due to outgassing (~ t-1^ )
- 3rd term -- pressure due to diffusion (~ t1/2^ and later exp(-Dt))
- 4th term -- pressure due to permeation (constant)
eff
K eff
D eff
eff O
S
Q
S
Q
S
Q
V
S t
P P + + +
= 0 exp
101103 105 107 109 101110131015 1017
10 10 - 10 - 10 - 10 - 10 - 10 - 10 -
103
Time (s)
Pressure
(Torr)
Volume ~ exp(-t)
Outgassing ~ t - Diffusion ~ t -1/ Permeation
Vacuum Technology
Page 10
Classificatoins
• Pressure Ranges
– 760 torr - 1x10 -3^ torr (essentially viscous flow -
roughing pumps
– 10 torr - 10 -5^ torr (transition flow range) - high
throughput pumps
– 10 -3^ torr - 10 -12^ torr (molecular flow) - high
vacuum pumps
Page 13
Mechanical Pumps
- 500-2000 rpm
- Single stage pumps
- Sp ~ 10-200 m^3 /hour
- Ultimate pressures ~ 1.5x10 -2^ Pa (~100μtorr)
Double Stage Rotary Vane
Vacuum Technology
Page 14
Mechanical Pumps
- Pumping speed of single versus double stage rotary vane
(sp ~ 30m^3 /hour)
Gas ballast introduces gas out exit port to
keep gases from condensing (ie water, acetone…)
Page 15
Mechanical Pumps
- Gas is drawn in during 1st revolution (A)
- After 1st revolution, that volume of gas is isolated from the inlet (B)
- During second revolution the gas is compressed and ejected
- ~40-600rpm
- Sp~30-1500 m^3 /hour
- Ultimate pressure ~ 10mtorr
Rotary Piston Pump
Vacuum Technology
Page 16
Mechanical Pumps
• Rotary vane and Rotary Piston Pump Issues
– Due to close tolerances (<0.1mm) the pump
surfaces are lubricated with oils
- Oil Properties
- Vapor Pressure - sets ultimate pressure of the pump
- Viscosity and wettability - lubrication
- Breakdown of oils and subsequent backstreaming
can be a significant source of contamination
Semiconductor manufacturers are going to “dry pumps”
Page 19
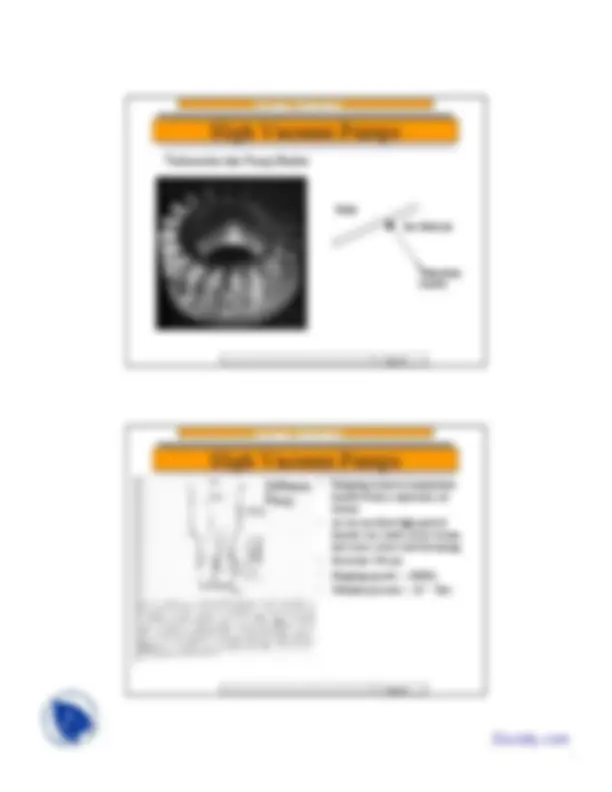
High Vacuum Pumps
Blade Gas Molecule
Momentum transfer
Turbomolecular Pump Blades
Vacuum Technology
Page 20
High Vacuum Pumps
- Pumping action by momentum transfer from a supersonic jet stream
- At viscous flow high particle density can scatter oil jet stream and cause severe backstreaming
- Need low VP oils
- Pumping speeds ~ 1000l/s
- Ultimate pressure ~ 10 -11^ Torr
Diffusion
Pump
Page 21
High Vacuum Pumps
- Diffusion pump pumping mechanism
- Low vapor pressure oil is heated to its boiling point
- Vapors flow up “chimney” and is ejected through a series of nozzles (supersonic velocities)
- The nozzles direct the vapor stream downward
- The gas stream is directed towared the water-cooled wall where is is condensed and returned to the boiler
- Gas particles that diffuse into this region are on average given a downward momentum and eventually ejected through the outlet
Vacuum Technology
Page 22
High Vacuum Pumps
- Pumping action is by adsorbing gas molecules onto cold surfaces - Gas particles impinge on cooled surface and do not desorb
- Typically two stages
- Liquid N2 (~80K)
- Liquid helium (~20K)
- Need to rough chamber to molecular flow or pre-mature pump saturation can occur - must periodically regenerate (ie heat up and desorb gas)
- Pumping Speed ~ 1000l/s
- Ultimat Pressure ~10-13^ Torr
Cryosorption
Pump
Page 25
Summary of Vacuum Pumps