













Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
lab file for CHT kuk this is lab file only for computer hardware technology
Typology: Study notes
1 / 20

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!













Various Cables Cable is the medium through which information usually moves from one network device to another. There are several types of cable which are commonly used with LANs. In some cases, a network will utilize only one type of cable, other networks will use a variety of cable types. The type of cable chosen for a network is related to the network’s topology, protocol, and size.
1. Patch Cables A patch cable connects two network devices. Patch cables are typically CAT5 / CAT5e Ethernet cables linking a computer to a nearby network hub, switch or router. Ethernet patch cables are useful to those building home computer networks and also to travelers who need wired access to Internet connections such as those provided in hotel rooms. They are normally manufactured using stranded rather than solid sheathing in order to give them pliability that reduces risk of breakage when unplugging or carrying them. 2. Ethernet Crossover Cables A crossover cable directly connects two network devices of the same type to each other over Ethernet. Ethernet crossover cables are commonly used when temporarily networking two devices in situations where a network router, switch or hub is not present. 3. RJ-45 Connectors and Cables RJ45 is a standard type of connector for network cables. RJ45 connectors are most commonly seen with Ethernet cables and networks. RJ45 connectors feature eight pins to which the wire strands of a cable interface electrically. Standard RJ-45 pinouts define the arrangement of the individual wires needed when attaching connectors to a cable. Coaxial Cable - Coaxial cabling has a single copper conductor at its center. A plastic layer provides insulation between the center conductor and a braided metal shield (See fig. 3). The metal shield helps to block any outside interference. Although coaxial cabling is difficult to install, it is highly resistant to signal interference. In addition, it can support greater cable lengths between network devices than twisted pair cable.
Various Connections In PC - A term used describe the physical location of where another peripheral is connected to the computer. Below are related dictionary definitions for each of the connections shown above and somerelatedterms.PS/2port, USB, Serial port, Parallel Port, Video card (VGA,SVGA), Modem (telephoneRJ-11), Network (RJ-45) Sound Card (sound out or line out / sound in or line in / Microphone / MIDI(Joystick)) PS/2 - Often referred to as the mouse and/or keyboard port, the PS/2 port was developed by IBM and is used to connect a computer mouse or keyboard to an IBM compatible computer. The PS/2 port is a mini DIN plug that contains six pins and is still found on all IBM compatible computers. USB: Short for Universal Serial Bus, USB is a standard that was introduced in 1995 by Intel, Compaq, Microsoft and several other computer companies. USB 1.x is an external bus standard that supports data transfer rates of 12 Mbps and is capable of supporting up to 127 peripheral devices. Serial port – An Asynchronous port on the computer used to connect a serial device to the computer and capable of transmitting one bit at a time. Serial ports are typically identified on IBM compatible computers as COM (communications) ports. For example, a mouse might be connected to COM1 and a modem to COM2. With the introduction of USB, FireWire, and other faster solutions serial ports are rarely used when compared to how often they’ve been used in the past. To the right is a close up of a DB9 serial port on the back of a computer. Parallel port – Less commonly referred to as the Getronics interface or Getronics connector after the company that originally designed it, the port was later developed by Epson. The parallel port is found on the back of IBM compatible computers and is a 25-pin (type DB-25) computer interface commonly used to connect printers to the computer. Modem - Short for MODulator/DEModulator, the first modem was first released by AT&T in 1960 when it introduced its dataphone. The modem is a hardware device that enables a computer to send and receive information over telephone lines. The modem is responsible for converting the digital data used by your computer into an analog signal used on phone lines and then converting it back once received on the other end. Below are the three available types of modems that can be used in computers. Internal modem- that connects to a PCI slot inside a newer desktop computer or ISA slot on an older computer. External modem is located within a box and is hooked up externally to the computer, usually the Serial Ports or USB port.
A computer card is an expansion device that provides an existing computer with certain added capabilities. What these capabilities are depends of course on the computer card. Some examples of popular computer cards includes graphics card, sound card, LAN card, TV tuner card etc. Widely varying both in size, price, and purpose, these cards have the ability to make your computer perform functions or connect with external devices that it couldn’t have previously. PCI Slot – This board has 2 PCI slots. These can be used for components such as Ethernet cards(LAN), sound cards, and modems. PCI-E 16x Slot – There are 2 of them on this motherboard diagram, both are blue. These are used for your graphics card. With two of them onboard, you can run 2 graphics cards in SLI. You would only need this if you are a gamer, or working with high end video / graphics editing. These are the 16x speed versions, which are currently the fastest. PCI-E 1x Slot – Single slot – In the PCIe 1.x generation, each lane (1x) carries 250 MB/s compared to 133 MB/s for the PCI slots. These can be used for expansion cards such as Sound Cards, or Ethernet Cards. Video/Graphics Card- A video card, video adapter, graphics-accelerator card, display adapter or graphics card is an expansion card whose function is to generate and output images to a display. Many video cards offer added functions, such as accelerated rendering of 3D scenes and 2D graphics, video capture, TV-tuner adapter, MPEG-2/MPEG-4 decoding, FireWire, light pen, TV output, or the ability to connect multiple monitors (multi-monitor). Other modern high performance video cards are used for more graphically demanding purposes, such as PC games.
Soundcard – A sound card (also known as an audio card) is a computer expansion card that facilitates the input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under control of computer programs. Typical uses of sound cards include providing the audio component for multimedia applications such as music composition, editing video or audio, presentation, education, and entertainment (games). Many computers have sound capabilities built in, while others require additional expansion cards to provide for audio capability. Before the invention of the sound card, a PC could make one sound – a beep. Although the computer could change the beep’s frequency and duration, it couldn’t change the volume or create other sounds. At first, the beep acted primarily as a signal or a warning. Later, developers created music for the earliest PC games using beeps of different pitches and lengths. This music was not particularly realistic — you can hear samples from some of these soundtracks at Crossfire Designs. EthernetCard – An Ethernet card is one kind of network adapter. These adapters support the Ethernet standard for high- speed network connections via cables. Ethernet cards are sometimes known as network interface cards (NICs). The Ethernet card was created to build a Local Area Network (LAN). Once Ethernet cable is connected to the Ethernet cards of two or more computers over the LAN, one can transfer files and data. This can be carried out for external hardware such as printers and scanners when information from one computer needs to be transferred to another computer. TV-tunercard - A TV tuner card is a computer component that allows television signals to be received by a computer. Most TV tuners also function as video capture cards, allowing them to record television programs onto a hard disk. TV tuner technology that brings broadcast video and HDTV content into the PC.
In any computer system the hard disk is considered as the secondary memory device that is used for the primary data storage. The primary memory is obviously the RAM. But as the RAM is the primary memory it cannot be used for the purpose of the permanent data storage. Hence a secondary memory device is necessarily needed for the purpose of the data storage in any computer system. Apart from hard disk drive the tape storage media can also be used as the secondary storage device. But the hard disk drive is the most popularly used secondary memory device. The main reason for this is the access speed and the reliability of the data it can offer. In the case of the tape drives the access speed is much low and the data transfer is comparatively low than the hard disk drive. Since the primary memory that is the RAM is a non volatile memory hence it cannot be used as the permanent memory storage device. Hence the hard disk or the need for as a secondary memory device is needed in any computer. The primary function of the primary memory is to load the programs so that the CPU – Central Processing Unit can easily and speedily access and execute the instructions. The primary memory can only boot the computer system; but it the hard disk drive that is responsible for the loading and the proper functioning of any operating system. The operating system is a necessary for the computers to run to the expectations of the user. Hence the hard disk is a must for the loading of the hard disk drive. The importance of the primary memory is that it is a compulsion that is necessary for the start up of the computer. A computer can start up even without a hard disk. But since there is no operating system that is present in the computer hence it is not possible to load the operating system. The computer will display a message usually in such a situation stating that “Disk Boot Failure”. The information that is required to boot a computer is stored in the hard disk boot sector. Also the importance of the hard disk drive is to store the backup of the data or any information that is created by the user. Apart from the hard disk drives the other storage devices like the optical disks that are the CD ROM, DVD ROM etc can be used for the purpose of the backup of the data or user information. The floppy disks can also be used for the backup of the data. The hard disk specification should also match the expectations of the computers; that is the storage capacity and access speed.
CD-ROM drives are necessary today for most programs. A single CD can store up to 650 MB of data (newer CD-Rs allow for 700 MB of data, perhaps more with “over burn”). Fast CD-ROM drives have been a big topic in the past, but all of today’s CD-ROM drives are sufficiently fast. Of course, it’s nice to have the little bits of extra speed. However, when you consider CD-ROM drives are generally used just to install a program or copy CDs, both of which are usually done rarely on most users’ computers, the extra speed isn’t usually very important. The speed can play a big role if you do a lot of CD burning at high speeds or some audio extraction from audio CDs (i.e. converting CDs to MP3s). CD-R/RW (which stands for Recordable / Rewritable) drives (aka burners, writers) allow a user to create their own CDs of audio and/or data. These drives are great for backup purposes (backup your computer’s hard drive or backup your purchased CDs) and for creating your own audio CD compilations (not to mention other things like home movies, multimedia presentations, etc.). DVD-ROM drives can store up to 4 GB of data or about 6 times the size of a regular CD (not sure on the exact size, but suffice to say it’s a very large storage medium). DVDs look about the same and are the same size as a CD-ROM. DVD drives can also read CD-ROM drives, so you don’t usually need a separate CD-ROM drive. DVD drives have become low enough inprice that there isn’t much point in purchasing a CD-ROM drive instead of a DVD-ROM drive. Some companies even make CD burner drives that will also read DVDs (all in one). DVD’s most practical use is movies. The DVD format allows for much higher resolution digital recording that looks much clearer than VCR recordings. DVD recordable drives are available in a couple of different formats – DVD-R or DVD+R with a RW version of each. These are slightly different discs and drives (although some drives support writing to both formats). One is not much better than the other, so it really boils down to price of the media (and also availability of the media).
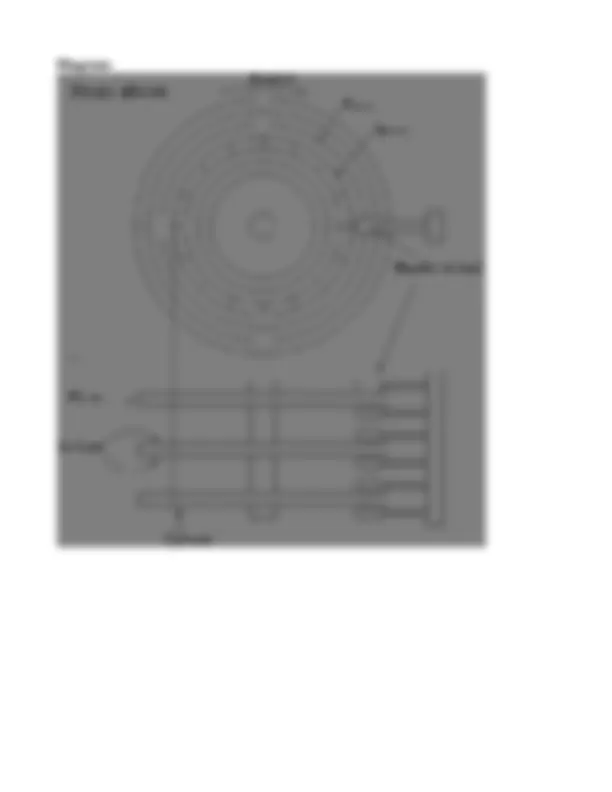
Motherboard Architecture:
1. Slot 1 Connector – This is where your Pentium II or Pentium III processor fits in. If you are using a standard Pentium, AMD K5 or K6, a Win Chip or an IBM/Cyrix processor then you will be using a Socket 7 (sometimes called Super 7 for the newer chips) motherboard and the connector will be as shown under the main diagram. 2. ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) Expansion Slots – Used to add expansion cards such as sound cards and internal modems. This type of expansion slot has a 16-bit bandwidth with a frequency of 8MHz. They are the older interface and are now being phased out. 3. PCI (Peripheral Component Interface) Slots – These are a newer type of expansion slot than the ISA ones and more components are now making use of them instead of the older slots. They have a 16-bit bandwidth and a frequency of 33MHz. 4. AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) – These are the newest standard in expansion slots, for use only with graphics boards. The newer model has a 64-bit bandwidth and a frequencyof66MHz. 5. Memory Slots – The ones shown are DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module) slots. Used to add memory to your computer. 6. Jumpers – These are used to configure the options on your motherboard, such as processor voltages etc. The jumper is placed over two pins to cause an electrical connection. Your motherboard manual should tell you the settings for each jumper. 7. Floppy disk and Primary/Secondary IDE channels – Used to interface you hard drives, CD-ROMS and floppy drives to your motherboard. The smaller connector is for the floppy drive, and the two larger ones are for IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) devices such as hard drives and CD-ROM drives. Up to two devices can be used from one channel, so on this motherboard you could have up to two floppy drives with four IDE devices. 8. Front Panel Connectors – These connect to the lights on the front of your system case to notify you of hard disk access, power etc. If you have an ATX style case then a power connector also fits here. The wires that should be connected to these come from the front of the case. 9. Real-Time Clock battery – Allows the computer to retain the time when it is powered down. Also
retains configuration data from when you first set up your computer.
10. BIOS EEPROM (Basic Input-Output System Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) – The BIOS configures the system resources on your system, and performs the self-check procedure each time you switch on your PC. 11. Ports – Connects external peripherals to the system such as a keyboard, mouse and printer. Most modern systems will have one each of PS/2 keyboard and mouse connectors, two serial ports, one parallel port and two Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports. 12. Voltage Regulation – These components help to regulate the power supply to prevent ‘spikes’ when the power is switched on. 13. Power Supply Connector – This is where the power arrives from your case’s PSU (Power Supply Unit). The one shown on this board is an ATX style connector and supports extra features such as auto shut-down and energy saving compatibility. The older AT style connectors have only a single row of pins and don’t support these extra features.
- 5 V power supply: This voltage is no longer used by any device and is retained only the purpose of backward compatibility with the older ISA slots. Originally, this voltage was used by some DRAM memory chips in original PC design. Micro channel system omitted this voltage from the power supply entirely. +3.3V power supply: Starting with the ATX designed in 1995 any system with ATX compatible power supplies include a 3. volt supply line from the power supply to the motherboard. Currently most CPUs & DRAM used 3.3V as well as some PCI adapter cards. Power Supply Control Signals: Although the primary function of the power supply is indeed to supply clean electrical power to systems, the power supply also interacts with the motherboard to perform an increasing number of functions, including CPU startup, system power down, voltage and temperature detection and other functions. Power Good Signal: The signal is actually a logic level signal designed as a power supply output signal to the CPU circuitry, to start the CPU running. Power On: Prior to the ATX standard, AT compatible power supplies either had the power switch mounted on the back or side of power supply itself, or had a remote switch mounted on the front panel. The power on signal wire is a part of ATX standard and carries only a low voltage logic level signal from the motherboard to the power supply, telling it when to turn on and when to turn off.
to the component pin, it does not matter if you have connected excess pins, this will be fixed later. Step 4: Flux There are 2 purposes for flux in soldering: to prevent beading of the solder, and help the solder flow from the soldering iron to the circuit board. Flux will be used on this board to limit the amount of bridged connections made, and generally make the job easier.
Step 7: Solder Now that the solder has been removed, repeat step 5 for this side of the board. Step 8: Fix any remaining solder bridges Use the method described in the previous steps to remove any more bridges. Step 9: Clean with Rubbing Alcohol If water soluble solder was used, replace rubbing alcohol with water.