












Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An outline for a presentation on monitoring and evaluating (m&e) agriculture and rural development policies in developing countries. It discusses the importance of results indicators, the challenges of measuring agricultural output, and the role of indicators in the sector-wide approach (swap) to ard programs. The document also includes a list of nineteen priority indicators and a data framework for sources of data and tools for m&e analysis.
Typology: Slides
1 / 20

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!













1
WYE CITY GROUP MEETING
ON STATISTICS ON RURAL DEVELOPMENT AND
AGRICULTURE HOUSEHOLD INCOME ,
The ideal environment for establishing a good M&E system is where:
1. there is a strong and consistent _demand for information.
The less-than-ideal condition , on the other hand, is where:
1. demand for information is _weak.
Ethiopia maize yields:1996-
15000
15500
16000
16500
17000
17500
18000
18500
19000
19500
20000
1996199719981999200020012002200320042005
Yields (Kg/ha)
Target Actual
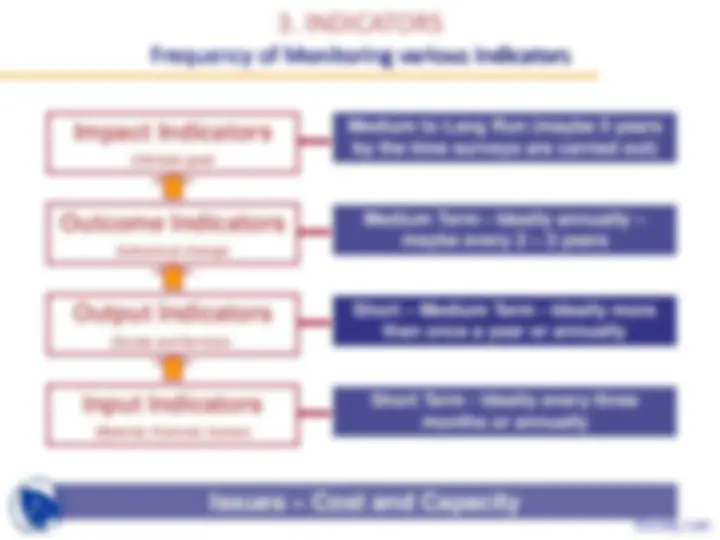
Detecting a trend in maize yields
7
(Ultimate goal)
(behavioral change)
(Goods and Services)
(Material, financial, human)
Medium to Long Run (maybe 5 years by the time surveys are carried out)
Medium Term - Ideally annually – maybe every 2 – 3 years
Short – Medium Term - Ideally more than once a year or annually
Short Term - Ideally every three months or annually
Countries : Cambodia, Nicaragua, Nigeria, Senegal, Tanania
Purpose : Test the conceptual framework and a preliminary list of
indicators against country capacity (M&E and Statistics), practice and learn lessons
Findings
All countries are engaged in strengthening and rationalising the national
M&E System in parallel with Statistical reform (NSDS)
Countries are at different stages regarding M&E and statistical
development (Examples of Senegal and Tanzania)
Disconnect between M&E and Statistical System
Outcome : Revised list of indicators, framework and good practices
Emerging Issues and challenges :
Decentralization and devolution=>implication for M7E and Stat system
Linkage and articulation between M&E and Statistics system
Linkages with international agencies
10
Subsector Total indicators
No. of generic indicators currently available
Cambodia Nicaragua Nigeria Senegal
The United Republic of Tanzania A. Core ARD sector indicators 28 8 7 9 8 3
B. Agribusiness and market development 13 2 4 4 3 3 C. Community-based rural development 9 2 4 2 D. Fisheries (aquaculture) 6 3 3 1 1 E. Forestry 13 5 3 3 5 3 F. Livestock 8 5 5 7 6 2 G. Policies and institutions 18 6 11 11 7 6 H. Research and extension 7 4 3 4 I. Rural Finance 7 5 5 4
J. Sustainable land and crop management 9 6 6 5 2
K. Water resource management 13 1 7 3 6 4 Total 131 40 56 56 38 27
11
1 Public spending on agriculture as a % of GDP from agriculture sector
11 % of the rural population using financial services of formal banking institutions 2 Public spending on agricultural input subsidies as a percentage of total public spending on agriculture
12 Public investment in agricultural research as a % of GDP from agriculture sector 3 Prevalence (%) of underweight children under five years of age in rural areas
13 Irrigated land as a % of crop land
4 Food production index 14 % change in sales/ turnovers of agro- enterprises 5 % annual growth in agricultural value added
15 % of farmers who are members of producer organizations 6 Rural poor as a proportion of total poor population
16 Agricultural withdrawal as % of total freshwater withdrawal 7 % change in yields of major crops of the country
17 Proportion (%) of land area formally establishes as protected area 8 % annual growth in value added in the livestock sub-sector
18 % change in soil loss from watersheds 9 Capture fish production as % of existing stock ( or a rating of state of major capture fish stocks relevant to exports and local food)
19 % land area for which there exists a legally recognized form of land tenure
10 Proportion of land area covered by forest (%) (see: menu of 86 indicators.doc)
Administrative information systems
Survey Programme of the CSO or MoA (Population census, Agricultural census, LSMS, DHS..)
Participatory Poverty Assessments
Financial Management Tools
17
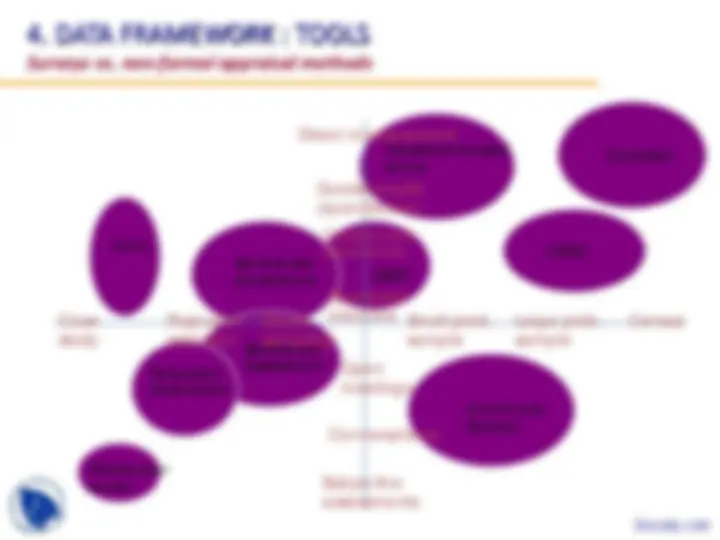
Comparison of key features of different surveys
1 2 3 4 5 Best used for :
Sample size Duration
Visits to household
Question- naire size Cost ($m)
Time series Sub- nat'l
Counter- factual
Population census Full coverage 3-6 months 1 4-8 15-25 ^ ^
Agricultural census 20 000-50 000 1-1.5 years 2-4 5-12 5-10 ^ ^
LSMS/integrated survey 5 000-10 000 1-1.5 years 2 40+ 1-2 ^ ^
Household budget survey 4 000-10 000 1-1.5 years 15-25 15-20 1-2 ^ ^
Community survey 100-500 4-6 months 1 4-6 0.2-0.4 ^ ^
Service delivery survey (CWIQ) 10 000-15 000 2-3 months 1 8 0.2-0.4 ^ ^
Focus group interviews 40-50 2-3 months 1-3 - 0.05-0.1 ^ ^
Windscreen survey 10-20 2-3 weeks 0 0.01 ^ ^
=not suitable =adequate =good
Opportunities
growing interest in the monitoring and evaluation of national development programmes=>growing interest in the rehabilitation of the NSS
NSDS process
Global strategy will provide:
Global Strategy to be discussed by senior experts during the upcoming International Statistical Institute Satellite meeting to be held 13-14 August 2009 in Maputo, Mozambique
A Sourcebook of indicators for monitoring and evaluation
20