








Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
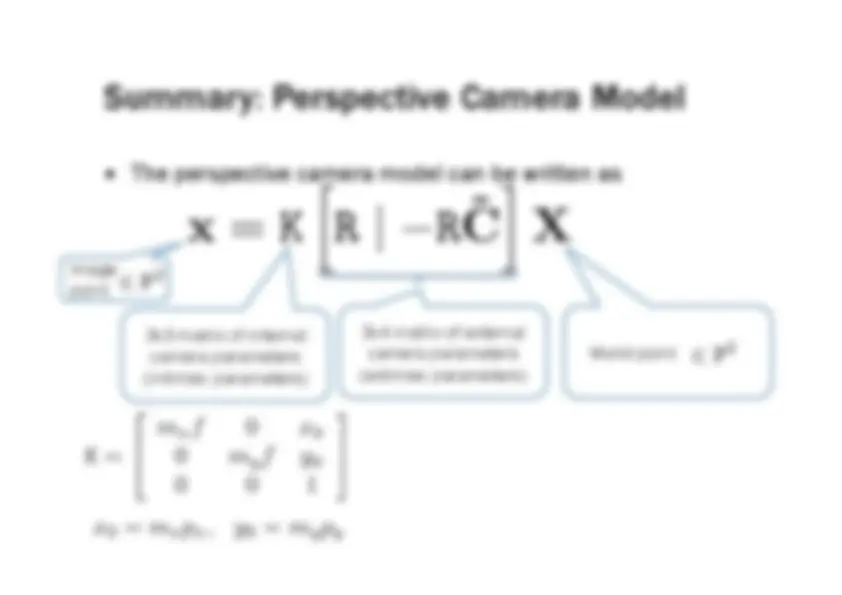
The perspective camera model, which can be represented by a 3x3 matrix of intrinsic parameters and a 3x4 matrix of extrinsic parameters. The intrinsic parameters include the focal length and principal point offset, while the extrinsic parameters represent the camera's position and orientation in the world. The document also includes examples of translation and rotation transformations.
What you will learn
Typology: Slides
1 / 13

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!








Camera Model Example
, rotated by φ along X , θ along Z, then
Figure Reference: Gonzales and Woods, “Digital Image Processing”
Camera Model Example ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎦ ⎤ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ ⎡ 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 3 2 1 r r r ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎦ ⎤ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ ⎡ − 0 0 0 1 0 sin cos 0 0 cos sin 0 1 0 0 0
⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎦ ⎤ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ ⎡ − 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 sin cos 0 0 cos sin 0 0
0 1 0 Y 0 0 0 1 Z 0 0 0 0 1 ! "
$ % & & & & & mx f 0 x 0 0 0 my f y 0 0 0 0 1 0 ! "
$ % & & & &
⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎦ ⎤ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ ⎡ − − − 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 3 2 1 r r r ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎦ ⎤ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ ⎡ − 0 0 0 1 0 sin cos 0 0 cos sin 0 1 0 0 0
⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎦ ⎤ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ ⎡ − 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 sin cos 0 0 cos sin 0 0
⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎦ ⎤ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ ⎡ − − − 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 Z Y X mx f 0 x 0 0 0 my f y 0 0 0 0 1 0 ! "
$ % & & & &
mx f 0 x 0 0 0 my f y 0 0 0 0 1 0
cos ω 0 −sin ω 0 0 1 0 0 sin ω 0 cos ω 0 0 0 0 1
cos τ sin τ 0 0 −sin τ cos τ 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
cos ϕ 0 −sin ϕ 0 0 1 0 0 sin ϕ 0 cos ϕ 0 0 0 0 1
0 cos β sin β 0 0 −sin β cos β 0 0 0 0 1
cos α sin α 0 0 −sin α cos α 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 −Δ Tx 0 1 0 −Δ Ty 0 0 1 −Δ Tz 0 0 0 1
cameraMat = perspective_transform * gimbal_rotation_y * gimbal_rotation_z * gimbal_translation * vehicle_rotation_x * vehicle_rotation_y * vehicle_rotation_z * vehicle_translation ;
c(1,1) = (cos(c_scn)cos(v_rll)-sin(c_scn)sin(v_pch)sin(v_rll))cos(v_hdg)-sin(c_scn)cos(v_pch)sin(v_hdg); c(1,2) = -(cos(c_scn)cos(v_rll)-sin(c_scn)sin(v_pch)sin(v_rll))sin(v_hdg)-sin(c_scn)cos(v_pch)cos(v_hdg); c(1,3) = -cos(c_scn)sin(v_rll)-sin(c_scn)sin(v_pch)cos(v_rll); c(1,4) = -((cos(c_scn)cos(v_rll)-sin(c_scn)sin(v_pch)sin(v_rll))cos(v_hdg)-sin(c_scn)cos(v_pch)sin(v_hdg))vx-(-(cos(c_scn)cos(v_rll)- sin(c_scn)sin(v_pch)sin(v_rll))sin(v_hdg)-sin(c_scn)cos(v_pch)cos(v_hdg))vy-(-cos(c_scn)sin(v_rll)-sin(c_scn)sin(v_pch)cos(v_rll))vz; c(2,1) = (-sin(c_elv)sin(c_scn)cos(v_rll)+(-sin(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+cos(c_elv)cos(v_pch))sin(v_rll))cos(v_hdg)+(-sin(c_elv)cos(c_scn)cos(v_pch)- cos(c_elv)sin(v_pch))sin(v_hdg); c(2,2) = -(-sin(c_elv)sin(c_scn)cos(v_rll)+(-sin(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+cos(c_elv)cos(v_pch))sin(v_rll))sin(v_hdg)+(-sin(c_elv)cos(c_scn)cos(v_pch)- cos(c_elv)sin(v_pch))cos(v_hdg); c(2,3) = sin(c_elv)sin(c_scn)sin(v_rll)+(-sin(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+cos(c_elv)cos(v_pch))cos(v_rll); c(2,4) = -((-sin(c_elv)sin(c_scn)cos(v_rll)+(-sin(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+cos(c_elv)cos(v_pch))sin(v_rll))cos(v_hdg)+(- sin(c_elv)cos(c_scn)cos(v_pch)-cos(c_elv)sin(v_pch))sin(v_hdg))vx-(-(-sin(c_elv)sin(c_scn)cos(v_rll)+(-sin(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch) +cos(c_elv)cos(v_pch))sin(v_rll))sin(v_hdg)+(-sin(c_elv)cos(c_scn)cos(v_pch)-cos(c_elv)sin(v_pch))cos(v_hdg))vy- (sin(c_elv)sin(c_scn)sin(v_rll)+(-sin(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+cos(c_elv)cos(v_pch))cos(v_rll))vz; c(3,1) = (cos(c_elv)sin(c_scn)cos(v_rll)+(cos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+sin(c_elv)cos(v_pch))sin(v_rll))cos(v_hdg)+(cos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)cos(v_pch)- sin(c_elv)sin(v_pch))sin(v_hdg); c(3,2) = -(cos(c_elv)sin(c_scn)cos(v_rll)+(cos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+sin(c_elv)cos(v_pch))sin(v_rll))sin(v_hdg)+(cos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)cos(v_pch)- sin(c_elv)sin(v_pch))cos(v_hdg); c(3,3) = -cos(c_elv)sin(c_scn)sin(v_rll)+(cos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+sin(c_elv)cos(v_pch))cos(v_rll); c(3,4) = -((cos(c_elv)sin(c_scn)cos(v_rll)+(cos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+sin(c_elv)cos(v_pch))sin(v_rll))cos(v_hdg)+(cos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)cos(v_pch)- sin(c_elv)sin(v_pch))sin(v_hdg))vx-(-(cos(c_elv)sin(c_scn)cos(v_rll)+(cos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+sin(c_elv)cos(v_pch))sin(v_rll))sin(v_hdg) +(cos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)cos(v_pch)-sin(c_elv)sin(v_pch))cos(v_hdg))vy-(-cos(c_elv)sin(c_scn)sin(v_rll)+(cos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch) +sin(c_elv)cos(v_pch))cos(v_rll))vz; c(4,1) = (1/flcos(c_elv)sin(c_scn)cos(v_rll)+(1/flcos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+1/flsin(c_elv)cos(v_pch))sin(v_rll))cos(v_hdg)+(1/ flcos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)cos(v_pch)-1/flsin(c_elv)sin(v_pch))sin(v_hdg); c(4,2) = -(1/flcos(c_elv)sin(c_scn)cos(v_rll)+(1/flcos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+1/flsin(c_elv)cos(v_pch))sin(v_rll))sin(v_hdg)+(1/ flcos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)cos(v_pch)-1/flsin(c_elv)sin(v_pch))cos(v_hdg); c(4,3) = -1/flcos(c_elv)sin(c_scn)sin(v_rll)+(1/flcos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+1/flsin(c_elv)cos(v_pch))cos(v_rll); c(4,4) = -((1/flcos(c_elv)sin(c_scn)cos(v_rll)+(1/flcos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+1/flsin(c_elv)cos(v_pch))sin(v_rll))cos(v_hdg)+(1/ flcos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)cos(v_pch)-1/flsin(c_elv)sin(v_pch))sin(v_hdg))vx-(-(1/flcos(c_elv)sin(c_scn)cos(v_rll)+(1/ flcos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+1/flsin(c_elv)cos(v_pch))sin(v_rll))sin(v_hdg)+(1/flcos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)cos(v_pch)-1/ flsin(c_elv)sin(v_pch))cos(v_hdg))vy-(-1/flcos(c_elv)sin(c_scn)sin(v_rll)+(1/flcos(c_elv)cos(c_scn)sin(v_pch)+1/ flsin(c_elv)cos(v_pch))cos(v_rll))vz+1;
3x3 matrix of internal camera parameters (intrinsic parameters) 3x4 matrix of external camera parameters (extrinsic parameters)
3 Image point
2