












Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
BIOD 171 MODULE 6 TEST QUESTIONS AND DETAILED ANSWERS 2025
Typology: Exams
1 / 23

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
















lOMoAR cPSD| 30
Correct!
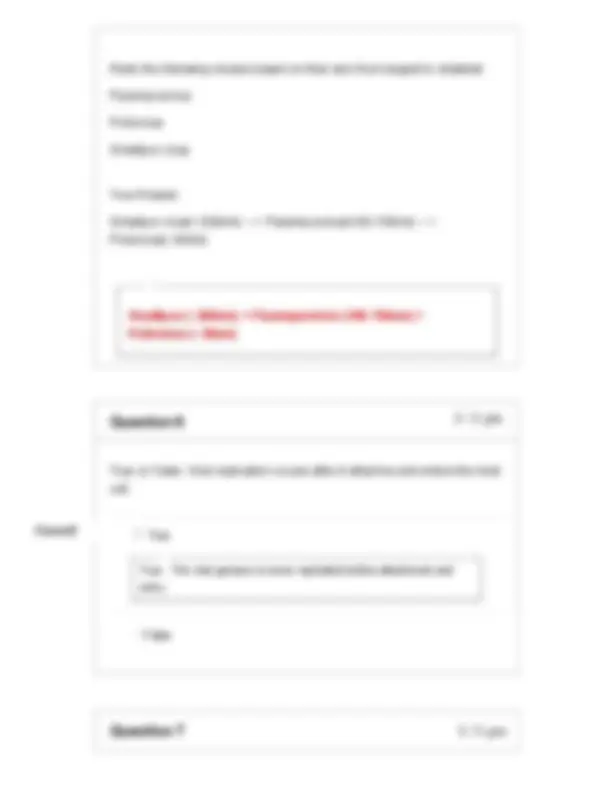
Describe the two basic components of a virus. Your Answer: Two basic components of a virus are; The genomic material that comprises of either DNA or RNA A capsid, a membraneus like protective structure that contains genetic materials similar to those of the eukaryotic cell A virus has (1) genomic material comprised of either DNA or RNA and (2) a capsid, a membrane-like protective structure that contains the genetic material, similar to the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
True or False. Although viruses may contain their genome within an enclosed space (much like the nucleus of a cell), it is considered neither eukaryotic nor prokaryotic. True False
Rank the following viruses based on their size from largest to smallest: Paramyxovirus Poliovirus Smallpox virus Your Answer: Smallpox virus(~200nm) ---> Paramyxovirus(100-150nm) ---> Poliovirus(~30nm) False
Smallpox (~200nm) > Paramyxovirus (100- 150 nm) > Poliovirus (~30nm) True or False: Viral replication occurs after it attaches and enters the host cell. Correct! (^) True True. The viral genome is never replicated before attachment and entry.
Place the following viral life cycle steps in order beginning with viral attachment and provide a description of each step. Uncoating: Release: Replication: Attachment: Entry: New infection: Your Answer: Attachment --> Entry --> Uncoating --> Replication --> Release --> New Infection Attachment; the viral receptors attaches to te host protein on the cell surface Entry; the virus fuses with the membrane of the host cells and enters the cell Uncoating; The viral capsid disassembles Replication; the viral genome is the blue print that replicates itself Release; New viral particles are produced and then released New Infection; the released new viral particles that exists the cell go ahead and infect new cells
Correct!
Identify the following components of a bacteriophage. 1 - [answer1] 2 - [answer2]
Describe the main differences between lytic and temperate phages. Your Answer: Lytic bacteriophage are inside the host bacteria and they keep replicating in the host until it ruptures and dies, on the other hand, the Temperate phages exist in the host bacteria but the do not replicate and they do not kill their host cells Lytic bacteriophages replicate within the host bacteria until it ruptures, whereas temporate (or lysogenic) phages primarily exist in a non-replicative state that does not kill the host cell. Lytic phages replicate all viral proteins needed for the assembly of new virus particles whereas lysogenic phage genomes are integrated into the host genome but production of viral proteins is suppressed.
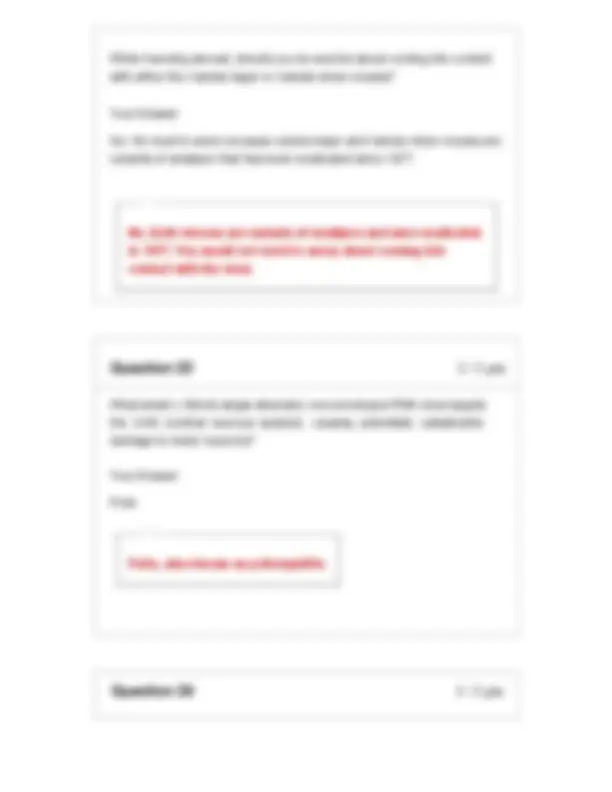
Based on the following image, would you expect the viral titer to be high or low? Why? Your Answer: Low. Viral titer is the quantitative amount of virus present in a culture or media. This sample shows cloudiness which indicates that there is a lot of intact bacteria present in it as turbidity shows the amount of intact bacteria present in a culture. But as the lytic cycle continues, the virus lyses on the bacteria cell and the sample becomes clearer. Low. As turbidity is a function of the number of intact bacterial cells present in the media, the amount of virus contained within the above tube must be low. As the lytic cycle continues more and more bacterial cells will be destroyed, effectively clearing the media.
Correct! Correct! Correct!
A patient diagnosed with German measles may additionally experience what disease? Select all that apply. A patient may experience a combination of symptoms such as fever, flu-like symptoms (influenza), cough, conjuctivitis, and a red blotchy skin rash. Impetigo Conjunctivitis Rheumatic fever Influenza-like symptoms
What disease displays as a secondary characteristic swelling of the testes/ovaries and pancreas? Your Answer: Mumps Mumps. A patient infected with mumps (aka epidemic paratitis) has primary swelling in the paratoid (salivary glands) located in the neck but also may have secondary swelling in the testes/ovaries and pancreas. Correct!
True or False. Similar to chickenpox, the blisters that appear with shingles can cover the entire body. Correct!
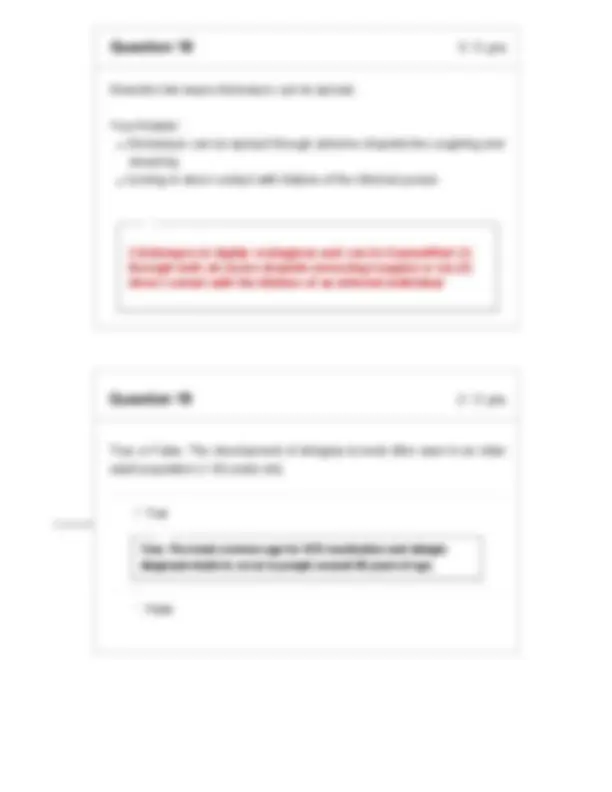
A person who has neither previously had chickenpox nor been administered the VZV vaccine is exposed to someone with an active VZV (shingles) outbreak and becomes infected. Explain why (or why not) the person will only develop shingles. Your Answer: The person who has niether previously had chickenpox nor been administered the VZU vaccine will first be infected with chickenpox and not shingles because shingles is the reactivation of dormant VZU form chickenpox infection. Hence someone who has never had chickenpox or been given the VZU vaccine will not have the dormant VZU from the chickenpox infection that they have never had or been vaccinated with in the first place. The infected individual will not develop shingles, but will develop chickenpox. Unvaccinated and unexposed individuals must first develop chickenpox, as shingles is the reactivation of the dormant VZV virus from the chickenpox infection.
By whom and where was the first polio vaccine developed? Your Answer:
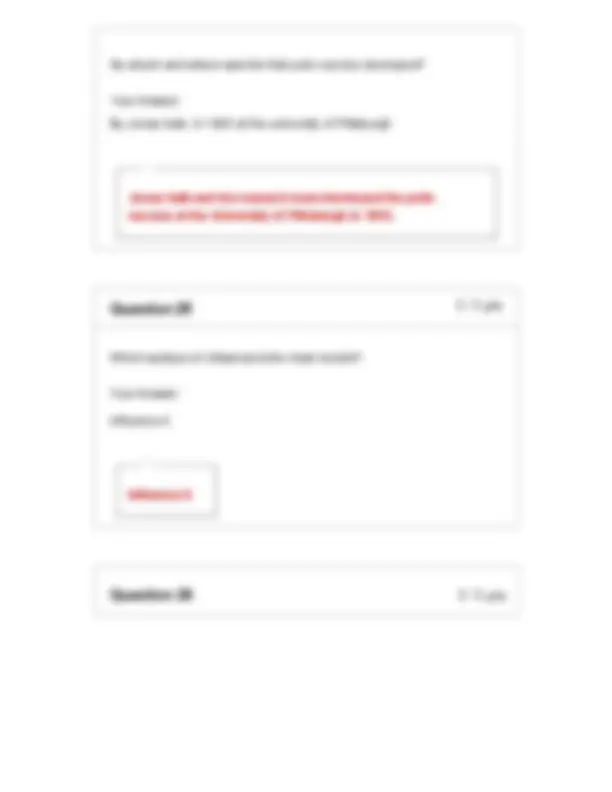
By Jonas Salk; In 1955 at the university of Pittsburgh Jonas Salk and his research team developed the polio vaccine at the University of Pittsburgh in 1955.
Which subtype of Influenza is the most virulent? Your Answer: Influenza A Influenza A
A drug company is trying to develop a new drug that will inhibit the release of newly produced viral particles. Would the drug company target hemagglutinin proteins or neuraminidase proteins? Why? Your Answer: Neuraminidase proteins should be targeted. This is because the Neuraminidase protein is responsible for the budding and release of the newly produced viral particles. unlike Hemagglutinin which is responsible for the attachment and entry of the virus. Its best adviced to target Neuraminidase which inhibits the release of newly produced viral particles Neuraminidase (N) proteins are directly involved in the budding and release of new viral particles and would thus be the correct target. Hemagglutinin (HA) proteins would not be advisable targets as they are directly involved in viral attachment and entry into the host cell.