




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Main points of this past exam are: Reduction Unit, Receives Power, Constant Angular Velocity, Transmitted Force, Transmitted, Shaft, Delivered, Pressure Angle, Opposing Force, Bearing Losses
Typology: Exams
1 / 6

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




Exam Code(s) 3BM, 3BG, 3BSE Exam(s) 3 rd^ Mechanical Engineering 3 rd^ Biomedical Engineering 3 rd^ Energy Systems Engineering
Module Code(s) ME Module(s) Mechanical Analysis and Design
Paper No. 1 Repeat Paper
External Examiner(s) Prof. Robin Clarke Internal Examiner(s) Dr. Padraig Molloy Prof. Sean Leen
Instructions: (^) Answer five questions, all questions will be marked
equally.
No. of Pages 5 Department(s) Mechanical & Biomedical Engineering Course Co-ordinator(s) Dr. Padraig Molloy
Requirements: MCQ Handout Statistical/ Log Tables Cambridge Tables Graph Paper Yes Log Graph Paper Other Materials Open Book Exam - Students permitted to bring in: Shigley’s Mechanical Engineering Design 9th^ Edition in SI units.
Release to Library: Yes
A gear reduction unit running at a constant angular velocity is shown in Figure Q1. Gear A receives power from another gear with the transmitted force F A , applied through a 20o pressure angle, as shown. The power is transmitted through the shaft and delivered through gear B, against an opposing force F B, at the pressure angle of 25o^ , as also shown.
(i) Determine the force F B , assuming no bearing losses. [2]
(ii) Find the magnitudes of the bearing reaction forces. [2]
(iii) Draw shear force and bending moment diagrams for the shaft in the horizontal and vertical planes. [3]
(iv) At the point of maximum bending moment determine the bending and torsional shear stresses. [6]
(v) At the point of maximum bending moment determine the principal stresses and maximum shear stress. [7]
Figure Q
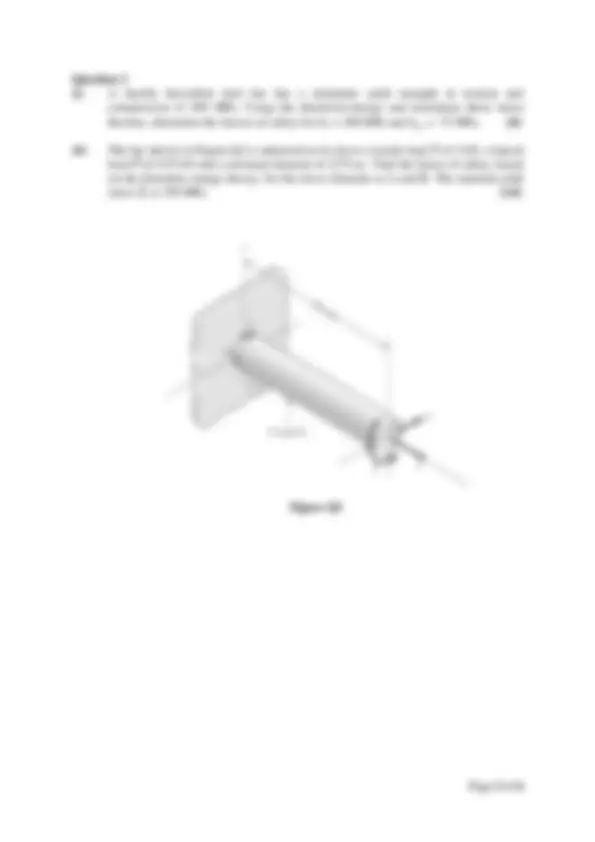
The steel used in the rotating shaft shown in Figure Q3 has a yield strength, S y, of 400 MPa and an ultimate strength S ut of 470 MPa. The shaft is subjected to a force of F of 5 kN. The fillet where shaft radius changes from 35 mm to 50 mm should be taken as the critical location for fatigue failure.
(i) Determine the static load factor of safety for failure by yielding. [8]
(ii) Determine the factor of safety for infinite life fatigue based failure. [12]
Figure Q
Question 4 (a) A single-threaded 25 mm diameter power screw has a pitch of 5 mm. The vertical load on the screw reaches 5 kN. The coefficients of friction are 0.08 for the collar and 0. for the threads. The collar frictional diameter is 50 mm. Find the overall efficiency and the torque required to raise and lower the load. [6]
(b) A M14 x 2 hexagonal head bolt is used to clamp together two 15 mm steel plates. Young’s modulus of the bolt and the plates can be taken as 207 GPa.
(i) Determine a suitable length for the bolt. [4]
(ii) Determine the bolt stiffness. [4]
(iii) Determine the stiffness of the members. [6]
A large spring is made of A227 hard drawn steel with a torsional modulus of elasticity, G , of 78.6 GPa. Wire diameter, d , is 3.5 mm, spring outside diameter D is 50 mm, spring free length L 0 is 74.6 mm and the total number of coils, N t , is 5.25. The spring has squared, ground ends.
(i) What is the factor of safety when this spring is compressed solid? [12]
(ii) What height can the spring be safely compressed to given a factor of safety n s = 1.5. [8]
Question 6 A full journal bearing is 28 mm long. The shaft journal has a diameter of 56 mm with tolerances of +0 and -0.012 mm. The bushing bore has a diameter of 56.05 mm, with tolerances of +0.012 mm and -0.0 mm. The bearing load is 2.4 kN and the journal rotates at 900 rpm. SAE 40 lubricating oil is used at a design operating temperature of 65o^ C. For the minimum clearance in the assembled bearing, find the following:
(i) The minimum oil film thickness. [6]
(ii) The power loss. [6]
(iii) The side-flow. [8]