












Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
basic electonics and electical
Typology: Summaries
1 / 21

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!














Half wave Rectifier Full wave Rectifier Bridge Rectifier
introduction
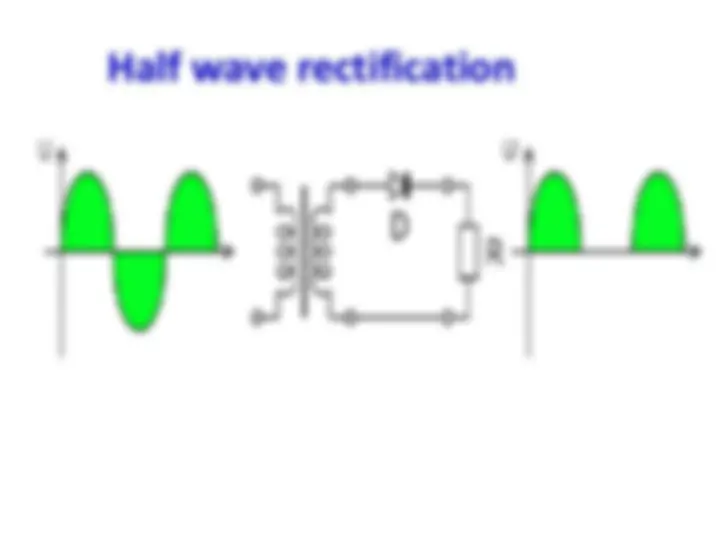
Half wave rectifier
In half wave rectification, either the positive or
negative half of the AC wave is passed, while the other half is blocked.
Because only one half of the input waveform reaches
the output, it is very inefficient if used for power transfer.
Half wave rectification
Output dc voltage calculation
The output DC voltage of a half wave rectifier can be calculated with the following two ideal equations
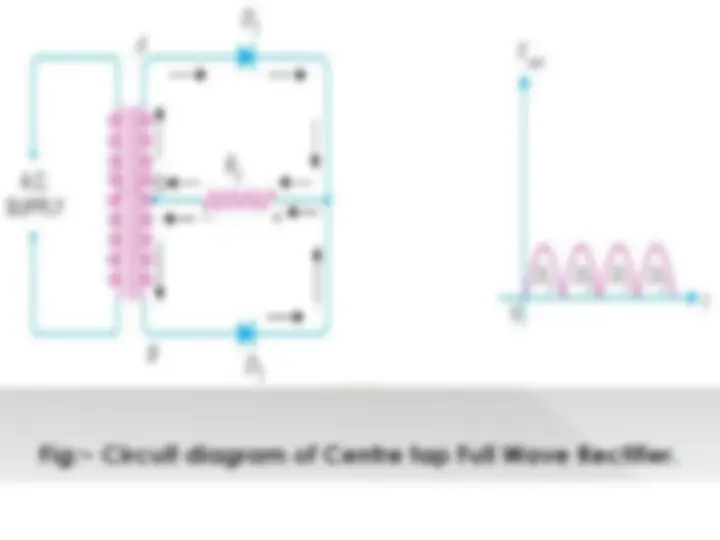
Full wave rectification
For single-phase AC, if the transformer is
center-tapped, then two diodes back-to- back (i.e. anodes-to-anode or cathode-to- cathode) can form a full-wave rectifier.
Full wave rectifier using transformer and 2 diodes
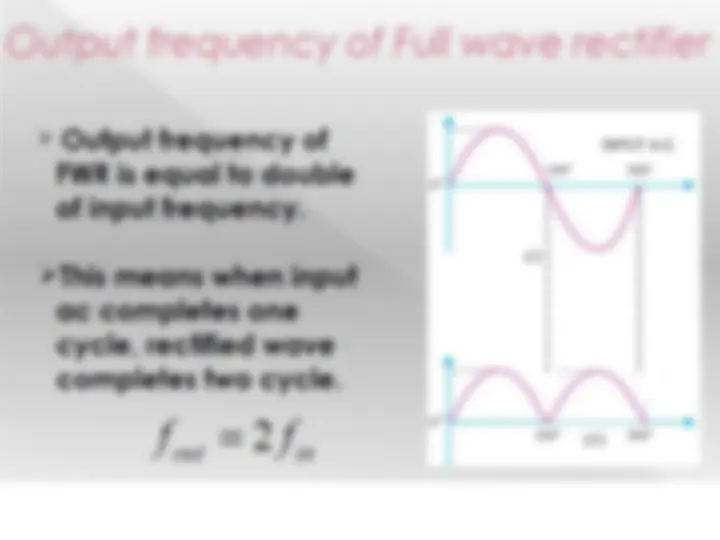
formula