




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Students who embark on A-level physics should be able to apply their knowledge from GCSE physics to solve problems in familiar and less familiar contexts.
Typology: Summaries
1 / 6

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




Students who embark on A-level physics should be able to apply their knowledge from GCSE physics to solve problems in familiar and less familiar contexts. The tasks in this summer work aim to improve your problem-solving skills and practical skills to give you a head start in A level Physics.
In year 12 Physics A level with AQA has 5 topics:
**1. Measurements and their errors
In this summer work you will be given tasks to introduce you to each of these 5 topics. For each topic you will be set
a) Seneca assignments (each one will take about 30 mins and will provide revision of GCSE topics and a simple introduction to AS. This needs to be completed online. You will get immediate feedback and can get more help with any topics you find difficult. b) A short question in the form ‘ What is a….? ’ for you to research independently. Just write a couple of sentences stating what you find out. Remember to give the reference of any website or book you find useful. c) A challenge. This may be a practical task for example. This is optional but try to do at least 2 challenges over the summer. d) An extension task eg in Isaac Physics. This is optional but highly recommended if you are hoping to achieve an A or A* in A level Physics.
TASK 1 Set up an account for Seneca
TASK 2 Set up an account for Isaac Physics
Some assignments have been set for you on isaacphysics.org. These problems can be completed online.
Join the group
There is a lot more to Isaac Physics than the assignments set for you. There are lots of questions
that you can choose from to work on independently. This will help you to develop the skills you’ll
need to thrive on university courses in Physics, Maths and Engineering etc. On the events page you
can find out about free Problem Solving workshops that are run.
1. Measurements and their errors a)Seneca assignments:
GCSE Required Practicals Paper 1
GCSE Required Practicals Paper 2
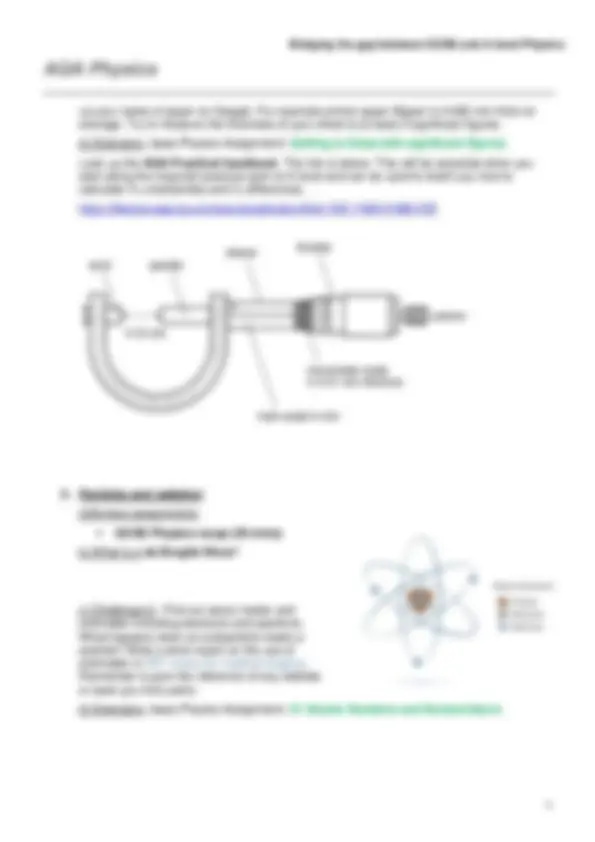
Measurements and errors b) What is a Vernier Scale? c) Challenge 1: Measure the thickness of a single sheet of A4 lined file paper. The only equipment you can have is a mm ruler, and a pile of paper. Plan a method to make your measurement as accurate and precise as possible. Write up your experiment and find the % difference between your measured value and the quoted value. To find the quoted value look
3. Waves
a)Seneca assignments: Bridging the Gap with waves Getting Ready for A level Physics
b) What is a Gravitational Wave? c) Challenge 3: Measure the speed of light using a microwave oven. There are several YouTube videos and other sites which can tell you how to measure the speed of light using a microwave oven and a bar of chocolate (or cheese, or marshmallows). Investigate standing waves first using the seneca assignments and see if you can do this experiment. (Make sure you have permission first and use an upturned plate so that it is easy to clean afterwards. d) Extension: Isaac Physics Assignment: 38 Wave properties and basic equations
4. Mechanics and materials a)Seneca assignments:
Bridging the Gap with mechanics b) What is an impulse? c) Challenge 4: Measure the acceleration due to gravity, g. The only equipment you can have is a mm ruler, a simple pendulum ( a small mass on the end of a long string) and a stopwatch (eg one on a phone).. Plan a method to investigate how the length of the pendulum affects the time for one complete swing (time period, T) of the pendulum. Vary and measure the length, L with the ruler and measure the time period, T with your stopwatch. Plot a graph of T^2 against L and draw a straight line of best fit. You can use excel or do it by hand if you have graph paper. One of the formula you will meet at A level states that T and L are linked by the equation
Use your graph to find g and calculate the percentage difference between your measured value and the quoted value, g = 9.81 m/s^2. https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/pendulum-lab/latest/pendulum-lab_en.html
d) Extension: Isaac Physics Assignment: Displacement and distance
B1 Components of a vector
5. Electricity a)Seneca assignments: Bridging the Gap with electricity
b) What is a superconductor? c) Challenge 5: Investigate the behaviour of 2 filament lamps , where one is brighter than the other. Build a circuit with 2 lamps in series and call the brighter lamp A and the dimmer lamp B. Now rebuild the circuit but with the 2 lamps in parallel. What do you notice about the brightness of the lamps now? You can build simple circuits like this using the simulation software:
https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/circuit-construction-kit-dc
Start by building a series circuit with 2 lamps and one cell. Click on one of the lamps to make its resistance larger than the other one. (eg 30 ohms and 10 ohms). This will be lamp A the brighter one. Now without changing the resistance change the circuit to a parallel one. Investigate the behaviour and record your observations carefully. Can you explain this result? You can explore further eg use ammeters and voltmeters to measure the current and potential difference in each circuit. Why is lamp A brighter in the series circuit but dimmer in the parallel circuit?
d) Extension: Isaac Physics Assignment: 27 Resistance and Power