











Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Introduction of Human Anatomy describes human skeleton system. Definition and composition of bones. Anatomical body planes. Gross and microscopic anatomy. Anatomical regions Upper and lower body extremity. muscles of legs.
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 18

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!











Introduction of
Anatomy
Human anatomy, also known as Anthropotomy, which refer
to the anatomical study of the human body or in other
words Anatomy is the science that studies the structure of
the body.
The human body is a biological system which is the groups
of organs that work together to produce and sustain life
Definition
and
Composition
of Bones
Bone is 1/3 (one third) connective tissue. It is impregnated
with which is filled with calcium salts which constitute the
remaining 2/3 (two third) of bone.
The composition of inorganic calcium salts is
mainly Calcium Phosphate partly Calcium Carbonate. This
composition make the bone hard and rigid, which can
afford resistance to compressive forces of weight-bearing
and impact forces of jumping.
The inorganic calcium salt is calcium hydroxy-apatite
[Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2]
Anatomical
Planes
geometric planes that divide
the human body into
sections. Mainly these body
planes are used in human
anatomy to describe the
direction and location of
body structures.
body:
plane: separates the front
(anterior) and back
(posterior) of the body
plane: separates the left
and right sides of the body
plane: separates the upper
(superior) and lower
(inferior) halves of the body
Human body
systems
There are 11 organ systems in the human body:
the central and autonomic systems
production
and nails, among other areas
Gross and
Microscopic
Anatomy
Gross anatomy related to the organs that can be seen
without the help of microscope such as a stomach,
whereas microscopic anatomy it indicates which is not
visible to the naked eye and must therefore be viewed with
the help of a microscope, such as the tiny microvilli that
line the crease of the stomach wall.
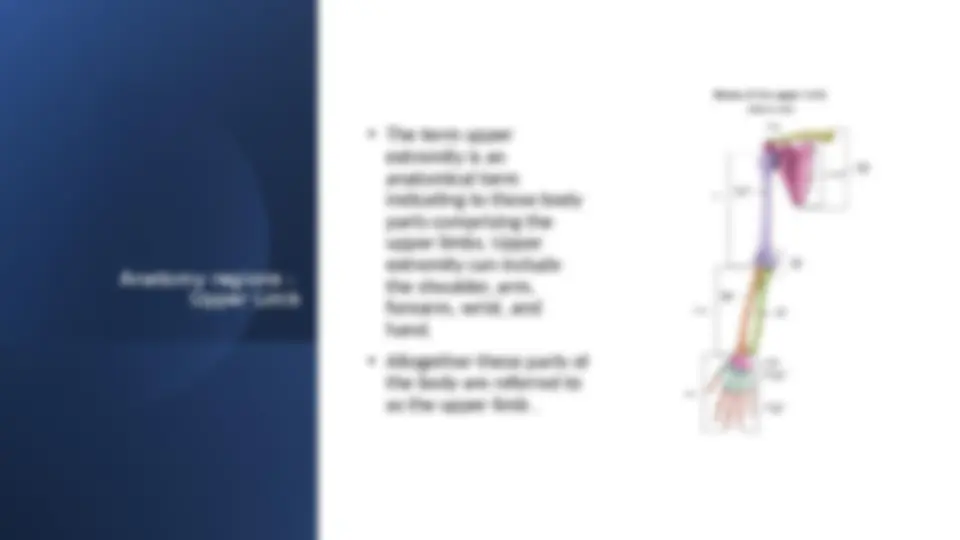
Shoulder Glenohumeral joint: humerus, scapula, clavicle
Muscles:
**- Superficial: deltoid, trapezius
Mnemonic: Rotator cuff SITS on the shoulder
Arm Bones: humerus
Nerves: they all originate from the brachial plexus
Arteries: branches of the brachial artery
Muscles:
Elbow Bones: humerus, radius, ulna
Movements: flexion, extension, pronation, supination
Forearm Bones: radius, ulna
Nerves: radial, ulnar, median nerves
Arteries: branches of the radial and ulnar arteries
Muscles:
Hand Bones: scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate,
metacarpals (5), phalanges (proximal, middle, distal)
Nerves: radial, ulnar, median nerves
Arteries: terminal branches of the radial and ulnar arteries
Muscles: thenar, hypothenar, metacarpal muscle groups
Upper limb
Muscle and
Movements
Scapula Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor, Subscapularis, Teres major,
Serratus anterior, Levator scapulae, Rhomboid major, Rhomboid
minor, Trapezius
Shoulder Pectoralis major, Pectoralis minor, Deltoid, Latissimus dorsi
Arm Brachialis, Biceps brachii, Coraco Brachialis, Triceps brachii
Forearm flexors Pronator teres, Flexor carpi radialis, Palmaris longus, Flexor carpi
ulnaris, Flexor digitorum superficialis, Pronator quadratus, Flexor pollicis
longus, Flexor digitorum profundus
Forearm extensors Supinator, Extensor digitorum, Extensor carpi ulnaris, Extensor carpi
radialis longus and brevis, Extensor indicis proprius, Extensor digiti
minimi, Brachioradialis
Hand Thenar eminence, Hypothenar eminence, Interossei, Lumbricals
Mnemonics: 'APB is A Friend Of Police' (thenar muscles
include Abductor Pollicis Brevis, Adductor pollicis, Flexor pollicis
brevis, Opponens Pollicis)
Bones of lower
extremity
talus (ankle bone), calcaneus (heel bone) Lower limb at a glance
Hip and pelvis
Bones: hip bones, saccrum, coccyx
Hip joint: ball and socket joint
Muscles: anterior and posterior (superficial, deep) groups
Arteries: gluteal and femoral arteries
Veins: external and internali iliac veins
Nerves: femoral cutaneous, femoral, obturator, sciatic and gluteal nerves, all branches of
the lumbosacral plexus
Thigh Bones: femur
Joints: hip and knee
Muscles: anterior, medial and posterior groups
Arteries: femoral artery and its branches
Veins: femoral vein, circumflex vein, long saphenous vein, and deep vein of the thigh
Nerves: femoral and sciatic nerves, branches from the lumbar and sacral plexuses,
respectively
Muscles of leg
tibialis anterior
extensor hallucis longus
extensor digitorum longus and
fibularis/peroneus tertius.
Muscles of leg
compartment consists of
seven (7)muscles in total
which is divided into
The superficial muscles are -
the triceps surae), and
and