





Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This is a ppt on address mapping in computer networks. This can be used for lecture notes as well
Typology: Slides
1 / 9

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!






The delivery of a packet to a host or a router requires The delivery of a packet to a host or a router requires
two levels of addressing:
two levels of addressing: logical
logical and
and physical
physical
. We need . We need
to be able to map a logical address to its corresponding to be able to map a logical address to its corresponding
physical address and vice versa. This can be done by physical address and vice versa. This can be done by
using either static or dynamic mapping. using either static or dynamic mapping.
Figure 21.1 ARP operation
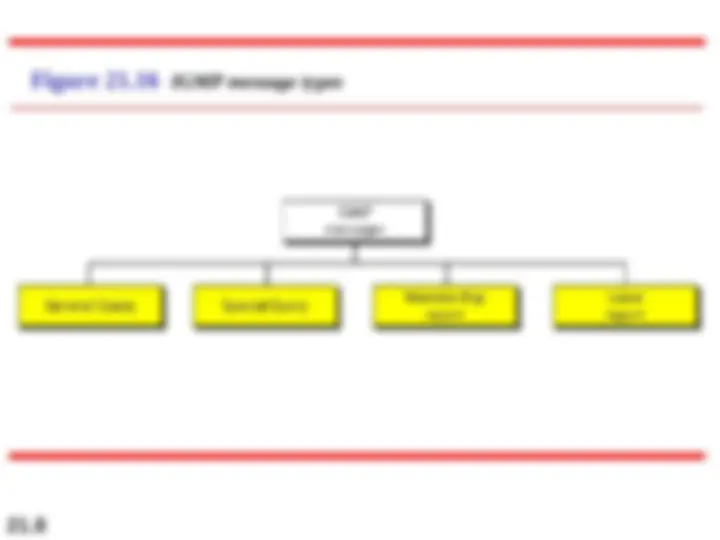
The IP protocol has no error-reporting or error- The IP protocol has no error-reporting or error-
correcting mechanism. The IP protocol also lacks a
correcting mechanism. The IP protocol also lacks a
mechanism for host and management queries. The mechanism for host and management queries. The
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) has been has been
designed to compensate for the above two deficiencies. designed to compensate for the above two deficiencies.
It is a companion to the IP protocol. It is a companion to the IP protocol.
Figure 21.8 General format of ICMP messages
The IP protocol can be involved in two types of The IP protocol can be involved in two types of
communication: unicasting and multicasting. The
communication: unicasting and multicasting. The
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is one Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is one
of the necessary, but not sufficient, protocols that is of the necessary, but not sufficient, protocols that is
involved in multicasting. IGMP is a companion to the involved in multicasting. IGMP is a companion to the
IP protocol. IP protocol.
Figure 21.16 IGMP message types